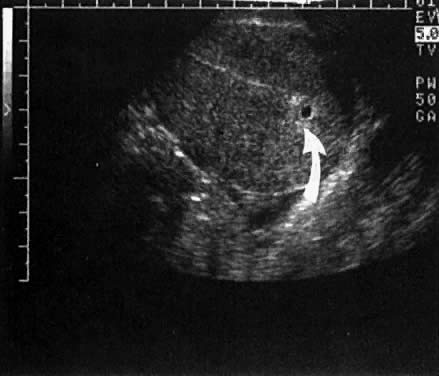
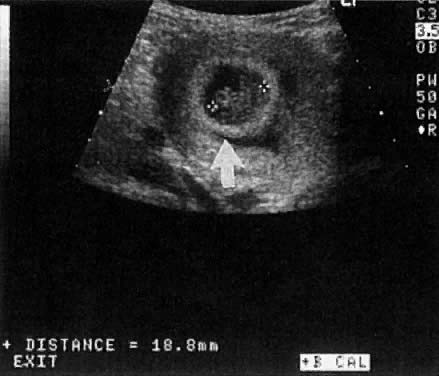
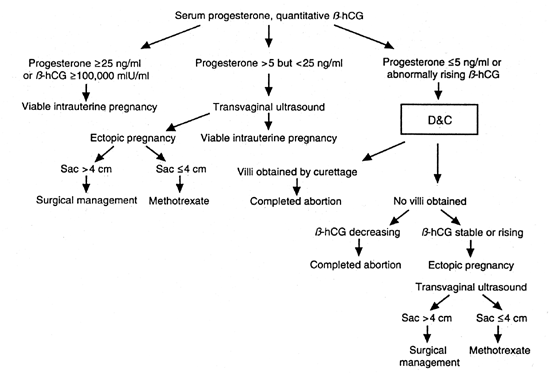
Warren and associates1 described the orderly appearance of gestational sac, yolk sac, and embryo with heartbeat at a given number of days from the onset of the last menstrual period (Table 1). With a transvaginal probe, a 3- to 4-mm gestational sac can usually be seen by 5 weeks from the last menstrual period (Fig. 1). A yolk sac or small fetal pole is usually seen by 6 menstrual weeks, when the mean diameter of the sac has reached 10 mm. As shown by Fossum and colleagues,2 the appearance of these structures can be correlated with β-human chorionic gonadotropin β-hCG) levels (Table 2). The literature regarding the correlation between quantitative β-hCG titers and early intrauterine gestational sacs and embryonic structures has been made somewhat confusing by the array of reference standards used to quantify β-hCG. Suffice it to say that the Third International Standard used by most companies marketing β-hCG kits corresponds roughly to the First International Reference Preparation.
TABLE 1 The Appearance of Early Gestational Structures
Days from LMP | 28–35 | 35–42 | 42–49 | 49–56 |
Gestational Sac | 100% | |||
Yolk Sac | 0% | 91% | 100% | |
Embryo with + FHTs | 0% | 0% | 86% | 100% |
LMP = last menstrual period; +FHTs = positive fetal heart tones
(Warren WB, Timnor-Trisch I, Peisner DB et al: Dating the early pregnancy by sequential appearance of embryonic structures. Am J Obstet Gynecol 161:747, 1989)
First IRP | Second IS | ||
Days from | β-hCG | β-hCG | |
Structure | LMP | (mIU/ml) | mIU/ml |
Sac | 35 | 1400 | 914 |
Fetal pole | 40 | 5100 | 3800 |
Heart motion | 47 | 17,200 | 13,200 |
LMP = last menstrual period; IRP = International Reference Preparation; IS = International Standard
(Fossum GT, Davajan V, Kletzky OA: Early detection of pregnancy with transvaginal ultrasound. Fertil Steril 49:788, 1988)
|
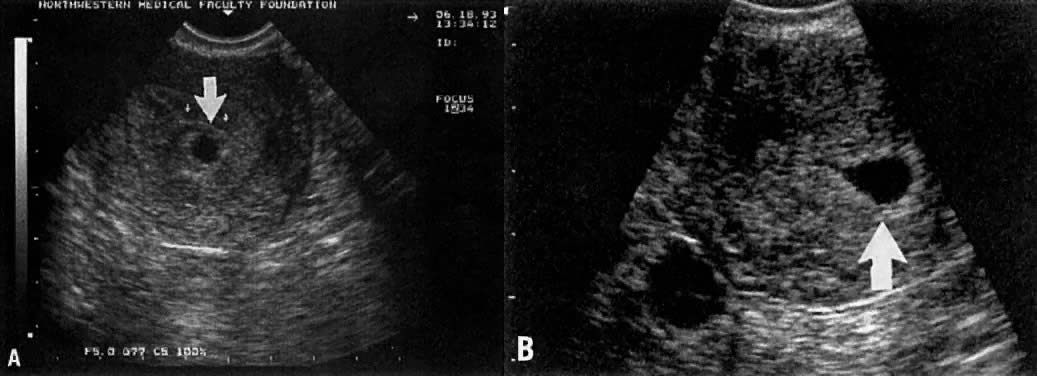
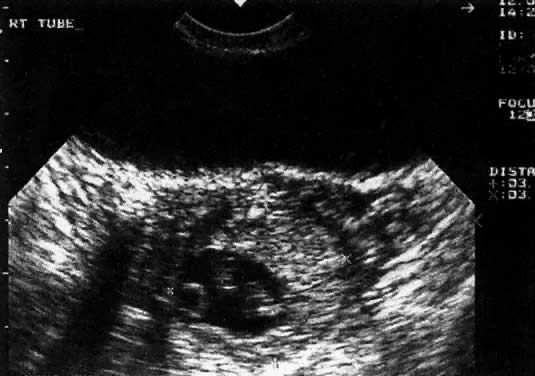
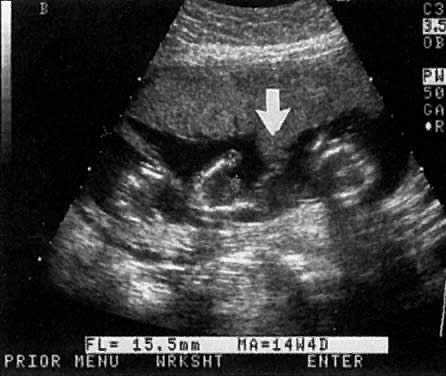
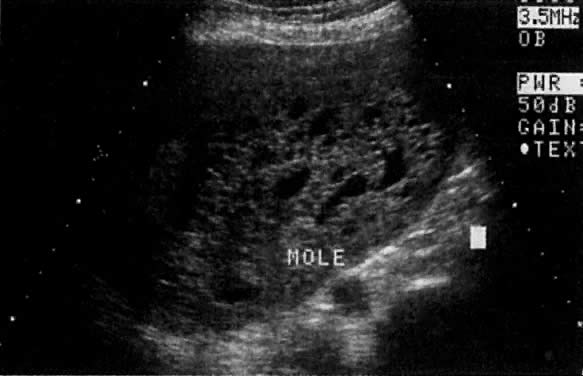
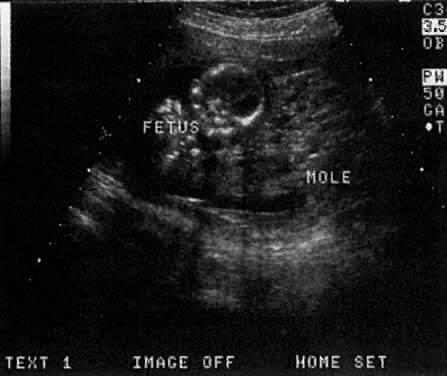
Considerable caution must be exercised not to confuse collections of fluid within a decidualized endometrium with early gestational sacs. These “pseudogestational sacs” can lead to a missed diagnosis of ectopic pregnancy. Normal early gestational sacs are seen eccentrically placed, adjacent to the echogenic central stripe (Fig. 2A and Fig. 2B). Even in experienced hands, pseudosacs and early gestational sacs can be confused.
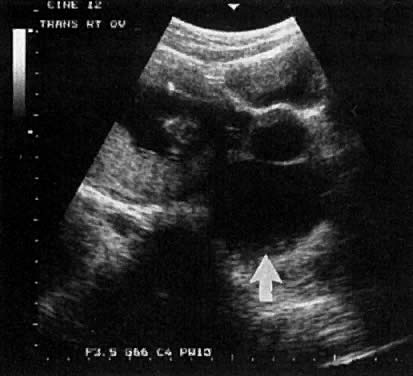
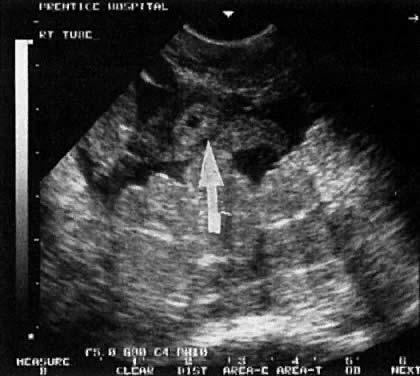
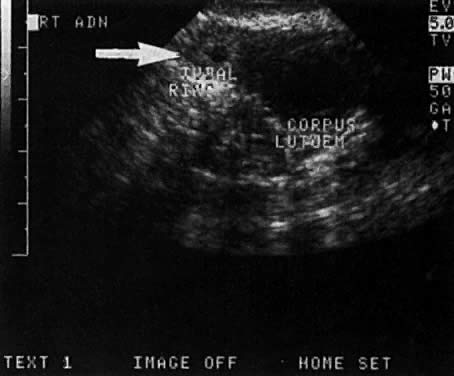
In the first 8 weeks of pregnancy, the corpus luteum is often identified as a cystic mass measuring 1 to 3 cm in diameter (Fig. 3), although they may reach as large as 8 cm.3 These masses usually resolve spontaneously by the onset of the second trimester. They can contain areas of complex echogenicity that may masquerade as a neoplasm or an ectopic pregnancy. Consultation with specialists should be obtained if an adnexal mass persists into the second trimester. The two most common benign neoplasms of the ovary during pregnancy are serous cystadenoma and benign cystic teratoma. The risk of a persistent adnexal mass during pregnancy subsequently diagnosed as malignant has probably been overestimated: it is significantly less than 1%.4 The place for expectant management of persistent adnexal masses thought to be benign by ultrasound criteria is controversial and currently being investigated.