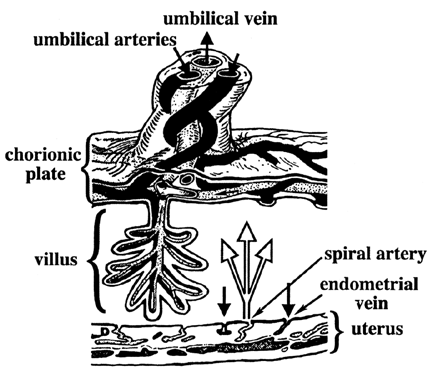
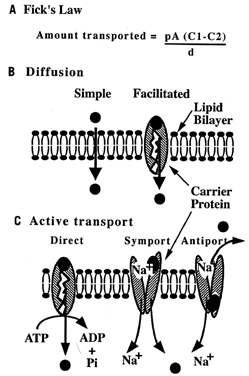
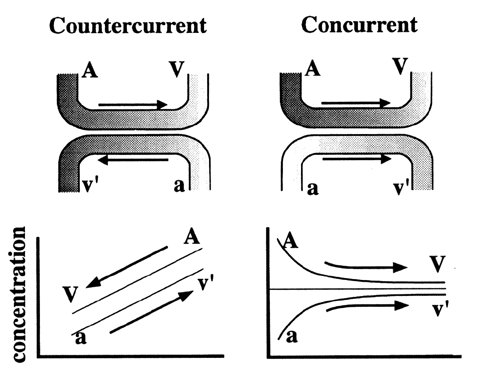
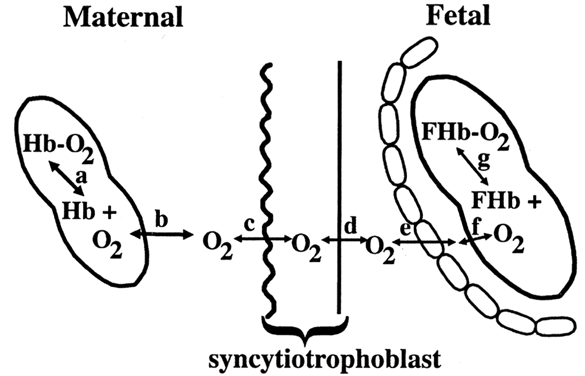
Carbohydrates Glucose is the principle substrate for energy metabolism. Glucose transporters
are located on the maternal (apical) and fetal (basal) surfaces
of trophoblast.17,18 These transporters belong to a class of glucose carrier proteins called
GLUT. All animal tissues contain GLUT proteins that allow facilitated
diffusion of glucose. The other class of glucose carrier proteins comprises
the SGLT proteins. These proteins actively transport glucose in
the gastrointestinal tract and renal tubules, but have not been identified
in the placenta. Like respiratory gases, placental transport of
glucose relies on a concentration gradient. Glucose transport can be
bidirectional, but under most conditions, flows from higher maternal concentration
to lower fetal concentration.19 This process occurs in two steps. The first gradient drives glucose across
the apical surface, from maternal blood to the intracellular compartment
of the syncytiotrophoblast. The second gradient drives glucose
across the basal surface, between syncytiotrophoblast and fetal blood. Most
of the gradient is due to the high glucose consumption of the placenta, which
may account for as much as 80% of the glucose uptake. Placental
glucose consumption declines when fetal serum glucose concentrations
are low, allowing a greater proportion of glucose to enter the
fetal circulation (Fig. 8).20 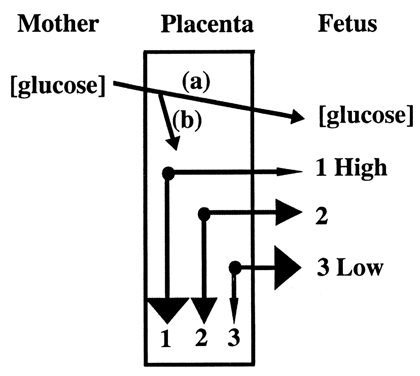 Fig. 8. Glucose is transported to the fetus down a concentration gradient ( a ). Fetal glucose concentration determines placental glucose transfer and
consumption ( b ). Compared to normal levels ( 2 ), at high fetal glucose concentrations, net diffusion from placenta to
fetus decreases and placental glucose consumption increases ( 1 ). A reciprocal effect occurs at low concentration ( 3 ).(Modified from Hay WW Jr: Energy and substrate requirements of the placenta
and fetus. Proc Nutr Soc 50:321, 1991) Fig. 8. Glucose is transported to the fetus down a concentration gradient ( a ). Fetal glucose concentration determines placental glucose transfer and
consumption ( b ). Compared to normal levels ( 2 ), at high fetal glucose concentrations, net diffusion from placenta to
fetus decreases and placental glucose consumption increases ( 1 ). A reciprocal effect occurs at low concentration ( 3 ).(Modified from Hay WW Jr: Energy and substrate requirements of the placenta
and fetus. Proc Nutr Soc 50:321, 1991)
|
Fetal glucose comes almost exclusively from placental transport. Most fetuses, including
the human fetus, require a glucose concentration of 4 to 8 mg/kg/min.21 The fetal brain, erythrocytes, and adrenal medulla rely entirely on glucose
as a metabolic fuel. There is a greater demand for nutrients as
the fetus grows. In the sheep, glucose utilization increases more than 10 fold
in mid gestation.22 This demand is met by an increase in placental surface area and a greater
diffusion gradient. The greater surface area of the placenta increases
the capacity fivefold (density of glucose transporter remains constant).23 The remainder of glucose demand is met by the growth of insulin-sensitive
fetal tissue. Insulin drives glucose into muscle, liver, and adipose
tissue, thus lowering the fetal serum concentration. The lower serum
concentration has two effects: (1) the gradient between fetal and maternal
blood increases; and (2) the placenta utilization of glucose decreases.19 The placenta consumes much of the glucose transported, metabolizing as
much as 50% to 70% to lactate.24 Trophoblasts use a small portion of the lactate, but export the majority
into maternal and fetal circulations. Early in pregnancy, the fetus
cannot utilize much of the lactate, and most lactate diffuses into the
maternal circulation. Late in pregnancy, more fetal tissues take up
lactate, which lowers fetal serum concentrations. This causes lactate
to diffuse into the fetal circulation. Lactate is believed to be an important
metabolic fuel, especially to the heart, as well as a substrate
for fetal growth. When maternal glucose concentrations are abnormal, there can be a marked
effect on the fetus. Because of facilitated diffusion, any elevation
in maternal glucose concentration results in an elevation in fetal serum
concentration. This may invoke an insulin response as early as 14 to 16 weeks' gestation.25 The net effect is to drive glucose into cells, which in turn lowers fetal
serum concentration. The magnitude of this response depends on the
amount of insulin-sensitive tissue present. If there is still an excess, glucose
diffuses back into the trophoblast. This increases placental
metabolism, to as high as 80% of the transported glucose, and potentially
decreases the fetal serum level by 60%.20 The placental response may have a greater effect but a slower response
than the fetal secretion of insulin. Sustained, mild increases in glucose
levels may therefore have limited fetal effect. However, if sharp
fluctuations in glucose occur, or if a marked increase in glucose concentration
occurs, insulin drives excess nutrients into fetal tissue. An
opposite response occurs with maternal hypoglycemia: fetal insulin
secretion drops, as well as placental utilization. This conserves the
glucose supply for nervous tissue, adrenals, and erythrocytes at the expense
of fetal growth. Amino Acids The placenta actively transports all amino acids, with fetal concentrations
exceeding maternal levels. Transporters are not specific, and are
grouped by the types of amino acids transferred and whether there is
a cotransport of sodium (Na+).26 The sodium-dependent systems are as follows: “A,” preferentially
transporting polar or neutral side chains (glycine and alanine); “ASC,” transferring alanine, serine, and cysteine; and XAG, selectively permeable to acidic amino acids (glutamate and aspartate). The
following are the sodium-independent pathways: “L,” open
to neutral, branched, and aromatic acids (leucine, phenylalanine); and
y+, transporting basic amino acids (lysine, ornithine, and arginine). Several
other amino acid transporters have been identified in the placenta
that do not fit into this simple classification.27 A dynamic interaction exists between placenta and fetal liver, producing
an amino acid pool for growth and metabolism. Both supply, modify, and
metabolize amino acids in the fetal circulation. For example, the placenta
actively takes up acidic amino acids (glutamate and aspartate) from
maternal blood, but transfers little to the fetus. In addition, certain
branched amino acids (leucine, isoleucine, and valine) are metabolized
to form glutamate. Trophoblast metabolizes as much as 80% of
the glutamate.28 There are two important consequences: (1) production of nicotinamide adenine
dinucleotide phosphate (NADPH), important in fatty acid and steroid
synthesis; and (2) reduction in glutamate concentration, a potential
neurotoxin. In animals, the placenta converts almost all of the transferred
maternal serine to glycine.29 This reaction can be linked to generation of tetrahydrofolate, an important
cofactor in metabolism. The net pool of amino acids transported
to fetal blood consists of maternally and placentally derived amino acids
and their metabolites. As blood enters the fetal liver via the umbilical vein, the hepatocytes
may take up and modify amino acids. The liver often performs reciprocal
functions to the placenta. For instance, it converts acidic and branched
amino acids into corresponding keto acid with release of ammonia (e.g., glutamine back to its keto acid, glutamate).28 Hepatocytes have the ability to produce amino acids de novo from ammonia.30 The total amino acid pool greatly exceeds fetal requirements for protein
synthesis. Fetal tissue utilizes some of the excess as another source
of energy, producing urea and ammonia and dumping these molecules into
the circulation. As fetal blood returns to the placenta, there is
active transport of amino acids. Because the urea cycle is negligible
in the placenta, there is constant production of ammonia. This dynamic
amino acid pool and ammonia supply are sources of nitrogen for building
blocks and metabolism. Unlike the respiratory gases and glucose, fetal amino acid concentrations
remain relatively stable over a large range of maternal values.31 Whether disruption of this process produces a fetal effect is unclear. Lower
fetal serum concentrations and decreased placental transport of
amino acids (specifically, branched amino acids) have been observed in
growth-restricted fetuses. In vitro, compounds associated with intrauterine
growth restriction (e.g., nicotine, ethanol, cocaine) decrease amino acid transport. Limiting supplies
of oxygen or glucose to the placenta decreases amino acid transport. Lipids Lipids play a major role in fetal growth and development. Lipids are a
basic constituent of plasma membranes, act as fuel for oxidative metabolism, and
are precursors for compounds such as prostaglandin. Unfortunately, we
have limited knowledge on lipid transport in the human placenta. Although
lipids play similar roles in other animals, there are striking
differences between animal models and humans. For instance, the
sheep fetus has only 3% body fat at birth, compared to 18% for the human
fetus. This difference is probably due to differences in lipid transport.19 Some conclusions have been drawn from a variety of animal models: (1) the
relative composition of lipids in the fetal serum is similar to that
in adults; (2) within a given species, fatter babies develop from mothers
with higher plasma concentrations of lipids; and (3) between species, there
is a relationship between lipid transport and fetal fat content.32 Thus, it is likely that fetal lipid content is dependent on the transplacental
concentration gradient. The human fetus has minimal carnitine and enzymes for lipid synthesis.33 As a result, the fetus depends on the placenta for most lipid requirements, for
the partial breakdown of fatty acids to medium and short chains, and
as a source of ketones. Lipids originate from the fatty acids
in the maternal blood. Once transported into the trophoblast, breakdown
occurs inside the mitochondria. Short- and medium-chain fatty acids
diffuse into the mitochondria without difficulty. Long-chain fatty acids
must be bound to carnitine, a derivative of lysine and methoin. Oxidation
then continues within the matrix space of the mitochondria. A
byproduct of lipid metabolism is the production of ketone bodies. For
synthesis, reversing oxidation in the mitochondria can produce long-chain
fatty acids from small and medium chains. More commonly, microsomes
produce fatty acids de novo from acetyl coenzyme A.34 In maternal serum, the majority of lipids do not circulate in a free form. Free
fatty acids are bound to albumin or are part of the chylomicron, whereas
cholesterol, triglyceride, and phospholipids are transported
as lipoprotein complexes.34 A membrane-bound enzyme, lipoprotein lipase, acts on chylomicrons and
lipoprotein complexes in maternal blood to liberate fatty acids. Some
lipids may diffuse directly across the membrane, whereas specific carrier
proteins transport fatty acids by facilitated diffusion.35 The trophoblast combines transported lipids with lipids produced de novo. From
the common pool, the trophoblast may oxidize lipids for cellular
energy or transport fatty acids directly into the fetal serum. More
important, the placenta produces medium- and short-chain fatty acids
and ketones and transports them to the fetus. Clinically, abnormal lipid transport may lead to abnormal fat content in
the fetus. Two points are important: (1) fetal and maternal concentrations
of lipids are similar; and (2) fatty acids in the fetal adipose
tissue come mainly from placental sources. Therefore, high maternal lipid
concentrations result in higher fat accumulation in adipose. This
may be seen in pregnant women with diabetes or hyperlipidemia. Water and Electrolytes Besides transport of nutrients, cells must maintain a specific ion composition
in the cytosol. The relative amounts of ions determine cell turgor
pressure, pH, and cellular metabolism. In all cells, intracellular
fluid contains a lower concentration of sodium and a higher concentration
of potassium. Trophoblasts must maintain this relationship and allow
for transport of the same water and ions to the fetus. The exact
mechanism is not well understood. Comparisons of fetal and maternal values
of selected ions are given in Table 2.36 Although the placenta contains a Na+:K+ pump at the basal (fetal) surface, net transfer of Na+ and Cl- is probably due to simple diffusion. Therefore, maternal and fetal
concentrations are similar. Increases or decreases of sodium or chloride
on one side are reflected by a proportional change on the other. In
contrast, fetal K+ concentration is tightly regulated, and is constant over a range of maternal
levels.37 TABLE 2. Maternal and Fetal Serum Concentrations of Selected Ions
Ion | Maternal Plasma (mM) | Fetal Plasma (mM) |
Sodium (Na+) | 138 ± 2 | 139 ± 4 |
Potassium (K-) | 4.6 ± 0.5 | 6.4 ± 0.2 |
Calcium (Ca2+) | 2.23 ± 0.12 | 2.81 ± 0.17 |
Chloride(Cl-) | 107 ± 2 | 108 ± 2 |
Phosphate (PO4-2) | 0.46 ± 0.20 | 0.62 ± 0.10 | (Shennan DB, Boyd CAR: Ion transport by the placenta: A review of membrane
transport systems. Biochem Biophys Acta 906:437, 1987)Water easily moves across placental tissue by osmosis, causing a high turnover
rate. At 14 weeks' gestation, the rate is 100 mL/hour, increasing
to a maximum of 3500 mL/hour at 35 weeks.38 In early pregnancy, osmosis occurs between three compartments: maternal
blood, fetal blood, and amniotic fluid. As the fetal skin becomes more
keratinized, less water is transferred from fetus to amniotic fluid
by osmosis, resulting in 95% of the maternal and fetal water exchange
occurring across the placenta.38 Although large amounts of water move across the placenta, the net transfer
is relatively balanced because the solute concentrations on either
side are similar. Accumulation of water into the fetal compartments
is 20 to 30 mL/day.39 Net transfer changes if the amount or concentration of solutes changes. Infusion
of hypotonic dextrose to mothers decreases solute concentration, increasing
net flow of water to the fetus. Hypertonic solutions, such
as mannitol, increase solute concentration; water moves from fetus
to mother, decreasing the net flow.40 Serum calcium exists in three forms: bound to protein (40%), as ion complexes (10%), and
free or ionized (50%). The placenta concentrates calcium
on the fetal side while maintaining a low intracellular level necessary
for cellular function. The exact mechanism is still unclear. Calcium
concentration is 10,000 times lower in intracellular fluid than
in extracellular fluid.41 Calcium channels are present at the maternal (apical) surface, allowing
ionized calcium to flow in by simple diffusion.42 Intracellular free calcium is sequestered to maintain a low intracellular
level. This sequestration of calcium may be in organelles, such as
the Golgi apparatus or endoplasmic reticulum, or bound to intracellular
protein, such as calcium-binding protein. Then trophoblasts actively
pump calcium into the fetal circulation via Ca-ATPase located on the
basal surface.43 Calcium demand increases greatly during the latter part of the pregnancy
as bone mineralization occurs (Fig. 9).44 It is not known how placenta transport changes to match demand. Levels
of calcium-binding protein increase dramatically in some animals, but
not in humans.45,46 Levels of Ca-ATPase do not increase in animal or human placentas.45 Regulation may occur via hormonal control. Severe maternal hypocalcemia (less
than 1.0 mmol), untreated hypoparathyroidism, and vitamin D deficiencies
have caused cases of neonatal rickets and hypocalcemia.47,48,49 In addition, the fetus may modify calcium transport via hormones. The
fetal parathyroid secretes parathyroid hormone and a parathyroid-related
protein.50 The fetal kidney and placenta can produce vitamin D.51 Both maternal and fetal hormones modify calcium transport in vitro, but
what roles they play in vivo still remain a mystery. Even less is known
about phosphate and magnesium transfer. Both minerals are concentrated
on the fetal side, and therefore active transport is likely to occur.44 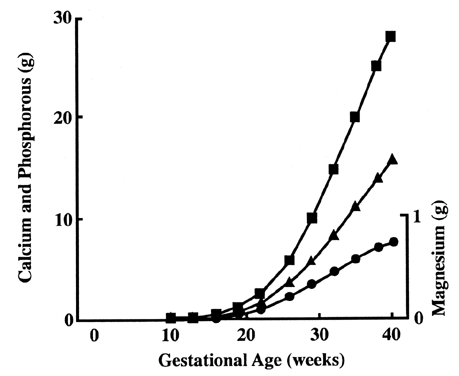 Fig. 9. Fetal accumulation of calcium (), phosphate (), and magnesium (·) during
pregnancy.[Widdowson EM: Changes in body composition during growth. In Davis
JA, Dobbing J (eds): Scientific Foundations of Pediatrics, p 330. London, William
Heinemann Medical Books, 1981] Fig. 9. Fetal accumulation of calcium (), phosphate (), and magnesium (·) during
pregnancy.[Widdowson EM: Changes in body composition during growth. In Davis
JA, Dobbing J (eds): Scientific Foundations of Pediatrics, p 330. London, William
Heinemann Medical Books, 1981]
|
|