The Alliance for
Global Women’s Medicine
A worldwide fellowship of health professionals working together to
promote, advocate for and enhance the Welfare of Women everywhere
Menu
Atlas of Obstetric Ultrasound
by The International Society of Ultrasound in Obstetrics & Gynecology
under the Editorship of Professor Gianluigi Pilu
Department of Obstetrics & Gynecology, Bologna, Italy
Contents:
- Early pregnancy and embryogenesis
- The gestational sac and the corpus luteum
- The corpus luteum
- The gestational sac in 2D ultrasound at 4–6 weeks' gestation
- The gestational sac in 3D ultrasound at 4–7 weeks' gestation
- A close look at the gestational sac at 7 weeks' gestation
- Embryo at 7–10 weeks' gestation
- Brain vesicles at 8 weeks' gestation
- Brain vesicles at 8 weeks' gestation: the unfolded embryo
- Casts of the cerebral vesicles at 7–10 weeks' gestation
- End of embryogenesis and beginning of fetal period: 11 weeks' gestation
- Fetal faces
- Placenta
- The fetal face
- 2D sonography of the fetal face
- 3D sonography of fetal face
- The fetal palate
- 3D ultrasound of the fetal skull
- 3D tomography of fetal face
- Varieties of fetal facial clefts
- Isolated cleft lip
- Cleft lip and palate
- Bilateral cleft lip and palate
- Facial anomalies with holoprosencephaly
- Lateral cleft of the fetal face
- Micrognathia
- Binder syndrome
- Apert syndrome
- Trigonocephaly
- Skin tag
- Beckwith Wiedemann syndrome
- The fetal brain
- Normal fetal brain at midgestation: basic survey
- Normal fetal brain at midgestation: advanced examination
- Fetal spine and neural canal
- Cerebral vessels
- Anencephaly throughout gestation
- Cephaloceles
- Myelomeningocele
- Myelocele
- Holoprosencephaly
- Facial anomalies with holoprosencephaly
- Agenesis of the septum pellucidum
- Complete agenesis of the corpus callosum
- Partial agenesis of the corpus callosum
- Megacisterna magna
- Dandy-Walker malformation
- Blake’s pouch cyst
- Vermian hypoplasia
- Cerebral lateral ventriculomegaly
- Types of cerebral lateral ventriculomegaly
- Intracranial hemorrhage
- Porencephalic cyst
- Schizencephaly: unilateral and bilateral
- Periventricular leukomalacia
- Brain findings with fetal cytomegalovirus infection
- Brain findings with fetal toxoplasmosis
- Intracranial arachnoid cysts
- Choroid plexus cyst
- Vein of Galen aneurysm
- Lissencephaly
- Unilateral megalencephaly
- Intracranial tumors
- The fetal heart
- Normal fetus situs
- Two-dimensional gray scale imaging of fetal cardiac connections
- Color Doppler of fetal cardiac connections
- The fetal aortic arch
- High definition flow of the fetal aortic arch
- Color Doppler of pulmonary veins
- Three-dimensional ultrasound of normal fetal heart
- Two-dimensional gray scale imaging of ventricular septal defects
- Color and pulsed Doppler of blood shunting across a muscular ventricular septal defect
- Muscular ventricular septal defect
- Inlet ventricular septal defect
- Outlet ventricular septal defect
- Perimembranous ventricular septal defect
- Apical ventricular septal defect
- Complete atrioventricular canal
- Partial atrioventricular canal
- Single ventricles
- Hypoplastic left heart syndrome
- Pulmonary atresia with intact ventricular septum
- Ebstein malformation of the tricuspid valve
- Tricuspid dysplasia
- Tetralogy of Fallot
- Complete transposition of great arteries
- Double outlet right ventricle
- Truncus arteriosus communis
- Interrupted aortic arch
- Coarctation/tubular hypoplasia of aortic arch
- Aortic stenosis
- Pulmonic stenosis
- Cardiac anomalies associated with isomerism
- Left isomerism
- Right isomerism
- Liver in isomerism
Early pregnancy and embryogenesis
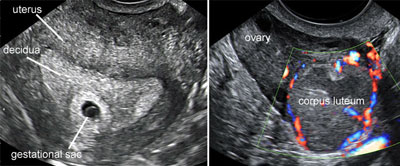
The gestational sac and the corpus luteum
Legend:The gestational sac and the corpus luteum
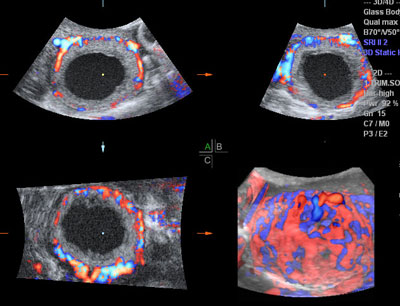
The corpus luteum
Legend:The corpus luteum
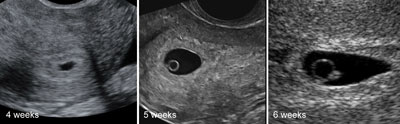
The gestational sac in 2D ultrasound at 4–6 weeks' gestation
Legend:The gestational sac in 2D ultrasound at 4–6 weeks' gestation
Reference(s):Oh JS, Wright G, Coulam CB. Gestational sac diameter in very early pregnancy as a predictor of fetal outcome. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 2002;20(3):267–9. PubMed PMID: 12230450.
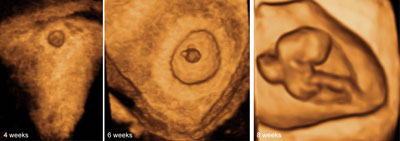
The gestational sac in 3D ultrasound at 4–7 weeks' gestation
Legend:The gestational sac in 3D ultrasound at 4–7 weeks' gestation
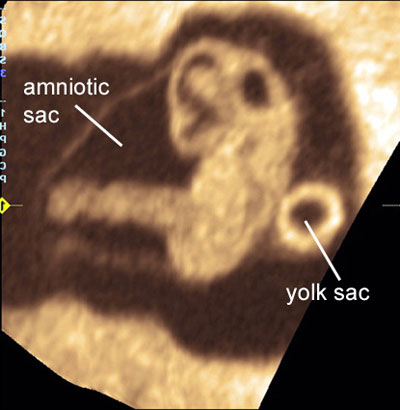
A close look at the gestational sac at 7 weeks' gestation
Legend:A close look at the gestational sac at 7 weeks' gestation
Reference(s):Grisolia G, Milano K, Pilu G, Banzi C, David C, Gabrielli S, Rizzo N, Morandi R, Bovicelli L. Biometry of early pregnancy with transvaginal sonography. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 1993;3(6):403–11. PubMed PMID: 12797241.
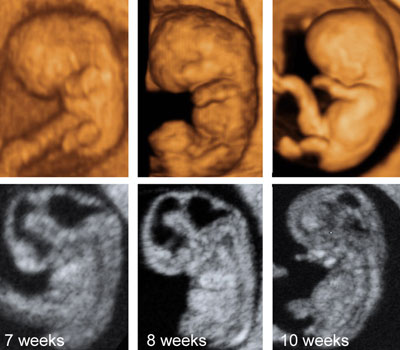
Embryo at 7–10 weeks' gestation
Legend:Sonography of the embryonic period with 3D (top) and 2D ultrasound. The developing cerebral vesicles are well seen
Reference(s):Blaas HG, Eik-Nes SH, Kiserud T, Hellevik LR. Early development of the forebrain and midbrain: a longitudinal ultrasound study from 7 to 12 weeks of gestation. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 1994;4(3):183–92. PubMed PMID: 12797178. Blaas HG, Eik-Nes SH, Kiserud T, Hellevik LR. Early development of the hindbrain: a longitudinal ultrasound study from 7 to 12 weeks of gestation. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 1995;5(3):151–60. PubMed PMID: 7788488. Blaas HG, Eik-Nes SH, Kiserud T, Berg S, Angelsen B, Olstad B. Three-dimensional imaging of the brain cavities in human embryos. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 1995;5(4):228–32. PubMed PMID: 7600202.
Brain vesicles at 8 weeks' gestation
Legend:Brain vesicles at 8 weeks' gestation
Reference(s):Blaas HG, Eik-Nes SH, Kiserud T, Hellevik LR. Early development of the forebrain and midbrain: a longitudinal ultrasound study from 7 to 12 weeks of gestation. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 1994;4(3):183–92. PubMed PMID: 12797178. Blaas HG, Eik-Nes SH, Kiserud T, Hellevik LR. Early development of the hindbrain: a longitudinal ultrasound study from 7 to 12 weeks of gestation. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 1995;5(3):151–60. PubMed PMID: 7788488. Blaas HG, Eik-Nes SH, Kiserud T, Berg S, Angelsen B, Olstad B. Three-dimensional imaging of the brain cavities in human embryos. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 1995;5(4):228–32. PubMed PMID: 7600202.
Brain vesicles at 8 weeks' gestation: the unfolded embryo
Legend:Brain vesicles at 8 weeks' gestation: the unfolded embryo
Reference(s):Blaas HG, Eik-Nes SH, Kiserud T, Hellevik LR. Early development of the forebrain and midbrain: a longitudinal ultrasound study from 7 to 12 weeks of gestation. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 1994;4(3):183–92. PubMed PMID: 12797178. Blaas HG, Eik-Nes SH, Kiserud T, Hellevik LR. Early development of the hindbrain: a longitudinal ultrasound study from 7 to 12 weeks of gestation. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 1995;5(3):151–60. PubMed PMID: 7788488. Blaas HG, Eik-Nes SH, Kiserud T, Berg S, Angelsen B, Olstad B. Three-dimensional imaging of the brain cavities in human embryos. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 1995;5(4):228–32. PubMed PMID: 7600202.
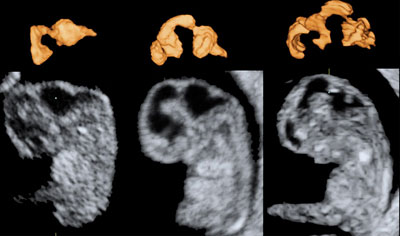
Casts of the cerebral vesicles at 7–10 weeks' gestation
Legend:Casts of the cerebral vesicles at 7–10 weeks' gestation
Reference(s):Blaas HG, Eik-Nes SH, Kiserud T, Hellevik LR. Early development of the forebrain and midbrain: a longitudinal ultrasound study from 7 to 12 weeks of gestation. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 1994;4(3):183–92. PubMed PMID: 12797178. Blaas HG, Eik-Nes SH, Kiserud T, Hellevik LR. Early development of the hindbrain: a longitudinal ultrasound study from 7 to 12 weeks of gestation. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 1995;5(3):151–60. PubMed PMID: 7788488. Blaas HG, Eik-Nes SH, Kiserud T, Berg S, Angelsen B, Olstad B. Three-dimensional imaging of the brain cavities in human embryos. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 1995;5(4):228–32. PubMed PMID: 7600202.
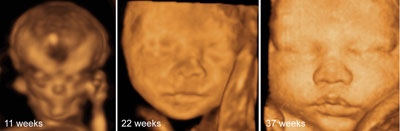
End of embryogenesis and beginning of fetal period: 11 weeks' gestation
Legend:End of embryogenesis and beginning of fetal period: 11 weeks' gestation
Fetal faces
Legend:Fetal faces
Reference(s):Rotten D, Levaillant JM. Two- and three-dimensional sonographic assessment of the fetal face. 1. A systematic analysis of the normal face. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 2004;23(3):224–31. PubMed PMID: 15027008.
Placenta
Normal placenta
Legend:Normal placenta
Normal umbilical cord
Legend:Normal umbilical cord
Placenta previa
Legend:Placenta previa
Reference(s):Oyelese Y. Placenta previa: the evolving role of ultrasound. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 2009;34(2):123–6. PubMed PMID: 19644942. Ghi T, Contro E, Martina T, Piva M, Morandi R, Orsini LF, Meriggiola MC, Pilu G, Morselli-Labate AM, De Aloysio D, Rizzo N, Pelusi G. Cervical length and risk of antepartum bleeding in women with complete placenta previa. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 2009;33(2):209–12. PubMed PMID: 19173235. Oppenheimer L, Holmes P, Simpson N, Dabrowski A. Diagnosis of low-lying placenta: can migration in the third trimester predict outcome? Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 2001;18(2):100–2. PubMed PMID: 11529986. Taipale P, Hiilesmaa V, Ylöstalo P. Transvaginal ultrasonography at 18-23 weeks in predicting placenta previa at delivery. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 1998;12(6):422–5. PubMed PMID: 9918091.
Placenta accreta
Legend:Placenta accreta
Reference(s):Hasegawa J, Matsuoka R, Ichizuka K, Mimura T, Sekizawa A, Farina A, Okai T. Predisposing factors for massive hemorrhage during Cesarean section in patients with placenta previa. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 2009;34(1):80–4. PubMed PMID: 19565529. Yang JI, Lim YK, Kim HS, Chang KH, Lee JP, Ryu HS. Sonographic findings of placental lacunae and the prediction of adherent placenta in women with placenta previa totalis and prior Cesarean section. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 2006;28(2):178–82. PubMed PMID: 16858740. Chou MM, Tseng JJ, Hwang JI, Ho ES, Lee YH. Sonographic appearance of tornado blood flow in placenta previa accreta/increta. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 2001;17(4):362–3. PubMed PMID: 11339200.
Velamentous insertion of the cord
Legend:Velamentous insertion of the cord
Reference(s):Sepulveda W, Rojas I, Robert JA, Schnapp C, Alcalde JL. Prenatal detection of velamentous insertion of the umbilical cord: a prospective color Doppler ultrasound study. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 2003;21(6):564–9. PubMed PMID: 12808673.
Vasa previa
Legend:Vasa previa
Reference(s):Catanzarite V, Maida C, Thomas W, Mendoza A, Stanco L, Piacquadio KM. Prenatal sonographic diagnosis of vasa previa: ultrasound findings and obstetric outcome in ten cases. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 2001;18(2):109–15. PubMed PMID: 11529988. Oyelese KO, Schwärzler P, Coates S, Sanusi FA, Hamid R, Campbell S. A strategy for reducing the mortality rate from vasa previa using transvaginal sonography with color Doppler. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 1998;12(6):434–8. PubMed PMID: 9918094. Fung TY, Lau TK. Poor perinatal outcome associated with vasa previa: is it preventable? A report of three cases and review of the literature. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 1998;12(6):430–3. Review. PubMed PMID: 9918093.
Chorioangioma of the placenta
Legend:Chorioangioma of the placenta
Reference(s):Quarello E, Bernard JP, Leroy B, Ville Y. Prenatal laser treatment of a placental chorioangioma. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 2005;25(3):299–301. Review. PubMed PMID: 15736199. Bermúdez C, Luengas O, Pérez-Wulff J, Genatios U, García V, Guevara-Zuloaga F, Quintero RA. Management of a placental chorioangioma with endoscopic devascularization and intrauterine transfusions. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 2007;29(1):97–8. PubMed PMID: 17201009. Sepulveda W, Aviles G, Carstens E, Corral E, Perez N. Placental chorioangioma. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 2000;16(6):597–8. PubMed PMID: 11169362. Jauniaux E, Ogle R. Color Doppler imaging in the diagnosis and management of chorioangiomas. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 2000;15(6):463–7. PubMed PMID: 11005112.
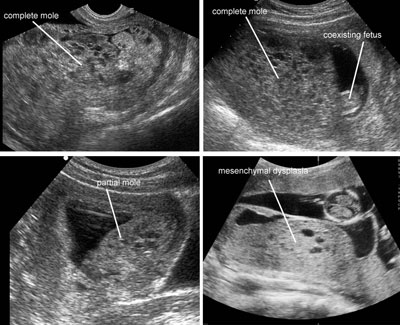
Molar pregnancy
Legend:Molar pregnancy
Reference(s):Kirk E, Papageorghiou AT, Condous G, Bottomley C, Bourne T. The accuracy of first trimester ultrasound in the diagnosis of hydatidiform mole. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 2007;29(1):70–5. PubMed PMID: 17201012. Fowler DJ, Lindsay I, Seckl MJ, Sebire NJ. Histomorphometric features of hydatidiform moles in early pregnancy: relationship to detectability by ultrasound examination. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 2007;29(1):76–80. PubMed PMID: 17171630. Johns J, Greenwold N, Buckley S, Jauniaux E. A prospective study of ultrasound screening for molar pregnancies in missed miscarriages. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 2005;25(5):493–7. PubMed PMID: 15818571. Sebire NJ, Rees H, Paradinas F, Seckl M, Newlands E. The diagnostic implications of routine ultrasound examination in histologically confirmed early molar pregnancies. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 2001;18(6):662–5. PubMed PMID: 11844211. Benson CB, Genest DR, Bernstein MR, Soto-Wright V, Goldstein DP, Berkowitz RS. Sonographic appearance of first trimester complete hydatidiform moles. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 2000;16(2):188–91. PubMed PMID: 11117091. Jauniaux E. Ultrasound diagnosis and follow-up of gestational trophoblastic disease. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 1998;11(5):367–77. Review. PubMed PMID: 9644780.
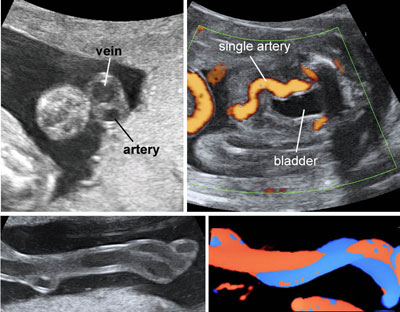
Single umbilical artery
Legend:Single umbilical artery
Reference(s):Rembouskos G, Cicero S, Longo D, Sacchini C, Nicolaides KH. Single umbilical artery at 11-14 weeks' gestation: relation to chromosomal defects. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 2003;22(6):567–70. PubMed PMID: 14689527. Raio L, Ghezzi F, Di Naro E, Cromi A, Buttarelli M, Sonnenschein M, Dürig P. Ductus venosus blood flow velocity characteristics of fetuses with single umbilical artery. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 2003;22(3):252–6. PubMed PMID: 12942496. Farrell T, Leslie J, Owen P. Accuracy and significance of prenatal diagnosis of single umbilical artery. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 2000;16(7):667. PubMed PMID: 11169377. Geipel A, Germer U, Welp T, Schwinger E, Gembruch U. Prenatal diagnosis of single umbilical artery: determination of the absent side, associated anomalies, Doppler findings and perinatal outcome. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 2000;15(2):114–7. PubMed PMID: 10775992. Raio L, Ghezzi F, Di Naro E, Franchi M, Brühwiler H, Lüscher KP. Prenatal assessment of Wharton's jelly in umbilical cords with single artery. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 1999;14(1):42–6. PubMed PMID: 10461337. Persutte WH, Hobbins J. Single umbilical artery: a clinical enigma in modern prenatal diagnosis. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 1995;6(3):216–29. Review. PubMed PMID: 8521073. Jauniaux E. The single artery umbilical cord: it is worth screening for antenatally? Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 1995;5(2):75–6. PubMed PMID: 7719870. Catanzarite VA, Hendricks SK, Maida C, Westbrook C, Cousins L, Schrimmer D. Prenatal diagnosis of the two-vessel cord: implications for patient counselling and obstetric management. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 1995;5(2):98–105. PubMed PMID: 7632225.
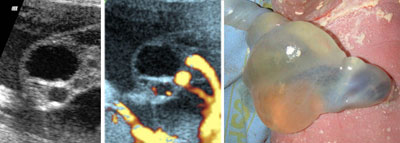
Umbilical cord cyst
Legend:Umbilical cord cyst
Reference(s):Ghezzi F, Raio L, Di Naro E, Franchi M, Cromi A, Dürig P. Single and multiple umbilical cord cysts in early gestation: two different entities. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 2003;21(3):215–9. PubMed PMID: 12666213. Sepulveda W. Beware of the umbilical cord 'cyst'. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 2003;21(3):213–4. PubMed PMID: 12666212. Battaglia C, Artini PG, D'Ambrogio G, Genazzani AR. Cord vessel compression by an expanding allantoic cyst: case report. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 1992;2(1):58–60. PubMed PMID: 12797010.
Cord hemangioma
Legend:Cord hemangioma
Abruptio placentae
Legend:Abruptio placentae
The fetal face
2D sonography of the fetal face
Legend:A combination of sagittal and coronal sections allows a detailed evaluation of the fetal face from early gestation
Reference(s):Ghi T, Perolo A, Banzi C, Contratti G, Valeri B, Savelli L, Morselli GP, Bovicelli L, Pilu G. Two-dimensional ultrasound is accurate in the diagnosis of fetal craniofacial malformation. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 2002 Jun;19(6):543–51. PubMed PMID: 12047531. Rotten D, Levaillant JM. Two- and three-dimensional sonographic assessment of the fetal face. 1. A systematic analysis of the normal face. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 2004;23(3):224–31. PubMed PMID: 15027008.
3D sonography of fetal face
Legend:3D ultrasound is an ideal tool for the evaluation of the fetal face
Reference(s):Merz E, Miric-Tesanic D, Welter C. Value of the electronic scalpel (cut mode) in the evaluation of the fetal face. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 2000;16(6):564–8. PubMed PMID: 11169352. Rotten D, Levaillant JM. Two- and three-dimensional sonographic assessment of the fetal face. 1. A systematic analysis of the normal face. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 2004;23(3):224–31. PubMed PMID: 15027008. Merz E, Benoit B, Blaas HG, Baba K, Kratochwil A, Nelson T, Pretorius D, Jurkovic D, Chang FM, Lee A; ISUOG 3D Focus Group. Standardization of three-dimensional images in obstetrics and gynecology: consensus statement. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 2007;29(6):697–703. PubMed PMID: 17523164.
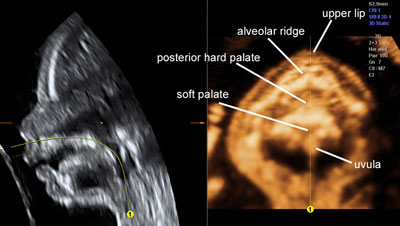
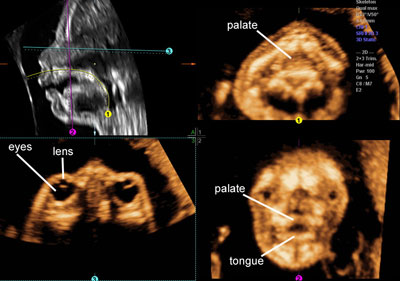
The fetal palate
Legend:3D ultrasound allows the visualization of the fetal palate
Reference(s):Platt LD, Devore GR, Pretorius DH. Improving cleft palate/cleft lip antenatal diagnosis by 3-dimensional sonography: the "flipped face" view. J Ultrasound Med 2006;25(11):1423–30. PubMed PMID: 17060428. Pilu G, Segata M. A novel technique for visualization of the normal and cleft fetal secondary palate: angled insonation and three-dimensional ultrasound. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 2007;29(2):166–9. PubMed PMID: 17111460. Ten PM, Pedregosa JP, Santacruz B, Adiego B, Barron E, Sepulveda W. Three-dimensional ultrasound diagnosis of cleft palate: 'reverse face', 'flipped face' or 'oblique face'--which method is best? Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 2009;33(4):399–406. PubMed PMID: 19109803.
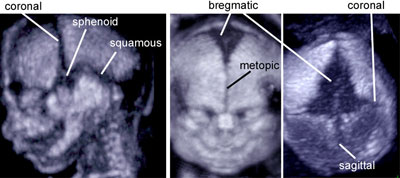
3D ultrasound of the fetal skull
Legend:The bones that form the fetal skull and the interposed sutures and fontanelles are visualized using an application of 3D ultrasound
Reference(s):Faro C, Benoit B, Wegrzyn P, Chaoui R, Nicolaides KH. Three-dimensional sonographic description of the fetal frontal bones and metopic suture. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 2005;26(6):618–21. PubMed PMID: 16193520.
3D tomography of fetal face
Legend:3D tomography of fetal face
Reference(s):Ghi T, Perolo A, Banzi C, Contratti G, Valeri B, Savelli L, Morselli GP, Bovicelli L, Pilu G. Two-dimensional ultrasound is accurate in the diagnosis of fetal craniofacial malformation. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 2002;19(6):543–51. PubMed PMID: 12047531. Platt LD, Devore GR, Pretorius DH. Improving cleft palate/cleft lip antenatal diagnosis by 3-dimensional sonography: the "flipped face" view. J Ultrasound Med 2006;25(11):1423–30. PubMed PMID: 17060428. Pilu G, Segata M. A novel technique for visualization of the normal and cleft fetal secondary palate: angled insonation and three-dimensional ultrasound. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 2007;29(2):166–9. PubMed PMID: 17111460. Ten PM, Pedregosa JP, Santacruz B, Adiego B, Barron E, Sepulveda W. Three-dimensional ultrasound diagnosis of cleft palate: 'reverse face', 'flipped face' or 'oblique face'--which method is best? Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 2009;33(4):399–406. PubMed PMID: 19109803.
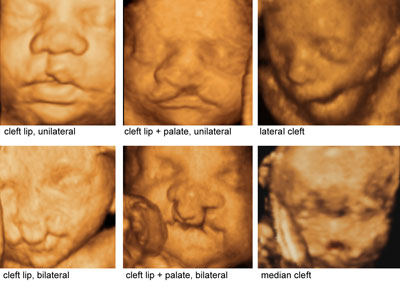
Varieties of fetal facial clefts
Legend:Varieties of fetal facial clefts
Reference(s):Rotten D, Levaillant JM. Two- and three-dimensional sonographic assessment of the fetal face. 2. Analysis of cleft lip, alveolus and palate. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 2004;24(4):402–11. PubMed PMID: 15343594. Pilu G, Visentin A, Ambrosini G, D'Antona D, Andrisani A. Three-dimensional sonography of unilateral Tessier number 7 cleft in a mid-trimester fetus. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 2005;26(1):98–9. PubMed PMID: 15909323. Ghi T, Perolo A, Banzi C, Contratti G, Valeri B, Savelli L, Morselli GP, Bovicelli L, Pilu G. Two-dimensional ultrasound is accurate in the diagnosis of fetal craniofacial malformation. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 2002;19(6):543–51. PubMed PMID: 12047531. Ten PM, Pedregosa JP, Santacruz B, Adiego B, Barron E, Sepulveda W. Three-dimensional ultrasound diagnosis of cleft palate: 'reverse face', 'flipped face' or 'oblique face'--which method is best? Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 2009;33(4):399–406. PubMed PMID: 19109803.
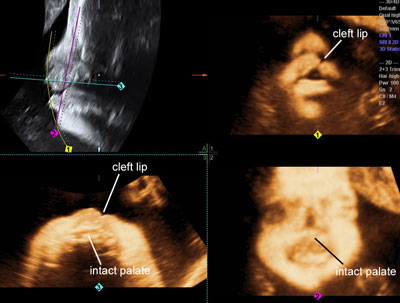
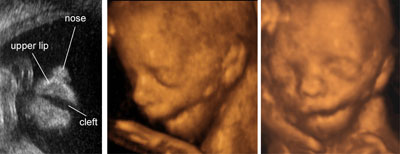
Isolated cleft lip
Legend:Isolated cleft lip
Reference(s):Rotten D, Levaillant JM. Two- and three-dimensional sonographic assessment of the fetal face. 2. Analysis of cleft lip, alveolus and palate. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 2004;24(4):402–11. PubMed PMID: 15343594. Ghi T, Perolo A, Banzi C, Contratti G, Valeri B, Savelli L, Morselli GP, Bovicelli L, Pilu G. Two-dimensional ultrasound is accurate in the diagnosis of fetal craniofacial malformation. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 2002;19(6):543–51. PubMed PMID: 12047531. Ten PM, Pedregosa JP, Santacruz B, Adiego B, Barron E, Sepulveda W. Three-dimensional ultrasound diagnosis of cleft palate: 'reverse face', 'flipped face' or 'oblique face'--which method is best? Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 2009;33(4):399–406. PubMed PMID: 19109803.
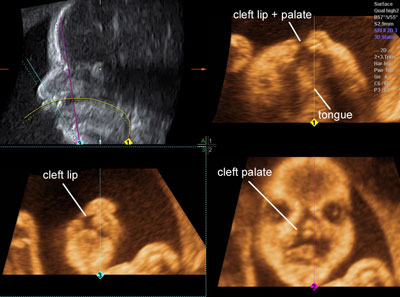
Cleft lip and palate
Legend:Cleft lip and palate
Reference(s):Rotten D, Levaillant JM. Two- and three-dimensional sonographic assessment of the fetal face. 2. Analysis of cleft lip, alveolus and palate. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 2004;24(4):402–11. PubMed PMID: 15343594. Ghi T, Perolo A, Banzi C, Contratti G, Valeri B, Savelli L, Morselli GP, Bovicelli L, Pilu G. Two-dimensional ultrasound is accurate in the diagnosis of fetal craniofacial malformation. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 2002;19(6):543–51. PubMed PMID: 12047531. Ten PM, Pedregosa JP, Santacruz B, Adiego B, Barron E, Sepulveda W. Three-dimensional ultrasound diagnosis of cleft palate: 'reverse face', 'flipped face' or 'oblique face'--which method is best? Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 2009;33(4):399–406. PubMed PMID: 19109803.
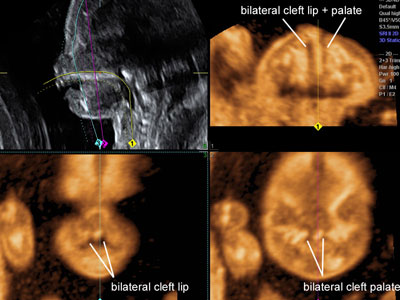
Bilateral cleft lip and palate
Legend:Bilateral cleft lip and palate
Reference(s):Rotten D, Levaillant JM. Two- and three-dimensional sonographic assessment of the fetal face. 2. Analysis of cleft lip, alveolus and palate. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 2004;24(4):402–11. PubMed PMID: 15343594. Ghi T, Perolo A, Banzi C, Contratti G, Valeri B, Savelli L, Morselli GP, Bovicelli L, Pilu G. Two-dimensional ultrasound is accurate in the diagnosis of fetal craniofacial malformation. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 2002;19(6):543–51. PubMed PMID: 12047531. Ten PM, Pedregosa JP, Santacruz B, Adiego B, Barron E, Sepulveda W. Three-dimensional ultrasound diagnosis of cleft palate: 'reverse face', 'flipped face' or 'oblique face'--which method is best? Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 2009;33(4):399–406. PubMed PMID: 19109803.
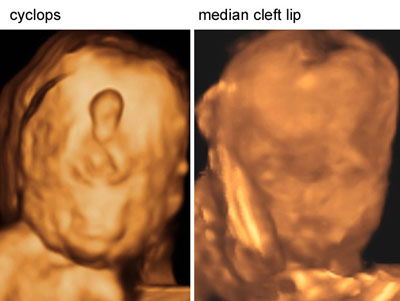
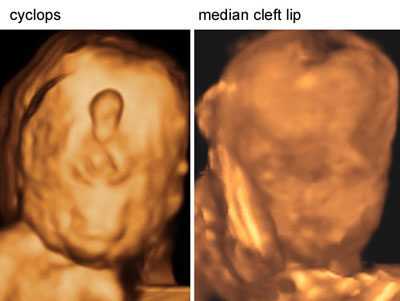
Facial anomalies with holoprosencephaly
Legend:Facial anomalies with holoprosencephaly
Reference(s):Blaas HG, Eriksson AG, Salvesen KA, Isaksen CV, Christensen B, Møllerløkken G, Eik-Nes SH. Brains and faces in holoprosencephaly: pre- and postnatal description of 30 cases. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 2002;19(1):24–38. PubMed PMID: 11851965. Blaas HG. Holoprosencephaly at 10 weeks 2 days (CRL 33 mm). Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 2000;15(1):86–7. PubMed PMID: 10776022. Blaas HG, Eik-Nes SH, Vainio T, Isaksen CV. Alobar holoprosencephaly at 9 weeks gestational age visualized by two- and three-dimensional ultrasound. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 2000;15(1):62–5. PubMed PMID: 10776015.
Lateral cleft of the fetal face
Legend:Lateral cleft of the fetal face
Reference(s):Pilu G, Visentin A, Ambrosini G, D'Antona D, Andrisani A. Three-dimensional sonography of unilateral Tessier number 7 cleft in a mid-trimester fetus. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 2005;26(1):98–9. PubMed PMID: 15909323.
Micrognathia
Legend:Micrognathia
Reference(s):Rotten D, Levaillant JM, Martinez H, Ducou le Pointe H, Vicaut E. The fetal mandible: a 2D and 3D sonographic approach to the diagnosis of retrognathia and micrognathia. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 2002;19(2):122–30. PubMed PMID: 11876802.
Binder syndrome
Legend:Binder syndrome or maxillo-nasal dysplasia can be diagnosed in early gestation. The prominent feature is the small nose with flattening of the fronto-nasal angle. It is frequently associated with other anomalies affecting mostly the fetal skeleton, malformations of the cervical spine, chondrodysplasia punctata and warfarin embryopathy
Reference(s):Cook K, Prefumo F, Presti F, Homfray T, Campbell S. The prenatal diagnosis of Binder syndrome before 24 weeks of gestation: case report. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 2000;16(6):578–81. PubMed PMID: 11169356.
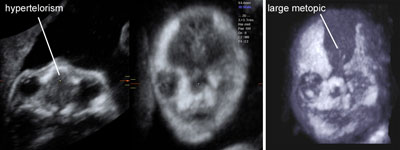
Apert syndrome
Legend:The combination of hypertelorism, a large metopic suture and finger abnormalities is suggestive of Aper syndrome
Reference(s):Faro C, Chaoui R, Wegrzyn P, Levaillant JM, Benoit B, Nicolaides KH. Metopic suture in fetuses with Apert syndrome at 22-27 weeks of gestation. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 2006;27(1):28–33. PubMed PMID: 16317802.
Trigonocephaly
Legend:An abnormal shape of the skull with a triangular forehead and a premature closure of the metopic suture is suggestive of trigonocephaly, a rare form of craniostenosis that is frequently associated with other anomalies
Reference(s):Chaoui R, Levaillant JM, Benoit B, Faro C, Wegrzyn P, Nicolaides KH. Three-dimensional sonographic description of abnormal metopic suture in second- and third-trimester fetuses. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 2005;26(7):761–4. PubMed PMID: 16308900.
Skin tag
Legend:Skin tag
Reference(s):Pilu G, Visentin A, Ambrosini G, D'Antona D, Andrisani A. Three-dimensional sonography of unilateral Tessier number 7 cleft in a mid-trimester fetus. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 2005;26(1):98–9. PubMed PMID: 15909323.
Beckwith Wiedemann syndrome
Legend:Beckwith Wiedemann syndrome is a rare congenital anomaly characterized by overgrowth and different patterns of anomalies including mostly omphalocele, macrosomia, macroglossia and placental dysplasia
Reference(s):Kotzot D. Prenatal testing for uniparental disomy: indications and clinical relevance. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 2008;31(1):100–5. Review. PubMed PMID: 18059071. Izbizky G, Elias D, Gallo A, Farias P, Sod R. Prenatal diagnosis of fetal bilateral adrenal carcinoma. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 2005;26(6):669–71. PubMed PMID: 16254889. Schwärzler P, Bernard JP, Senat MV, Ville Y. Prenatal diagnosis of fetal adrenal masses: differentiation between hemorrhage and solid tumor by color Doppler sonography. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 1999;13(5):351–5. PubMed PMID: 10380301. Jauniaux E, Nicolaides KH. Early ultrasound diagnosis and follow-up of molar pregnancies. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 1997;9(1):17–21. PubMed PMID: 9060124.
The fetal brain
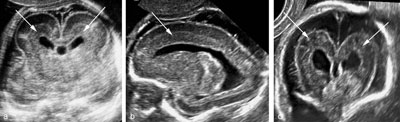
Normal fetal brain at midgestation: basic survey
Legend:Normal fetal brain at midgestation: basic survey
Reference(s):International Society of Ultrasound in Obstetrics & Gynecology Education Committee. Sonographic examination of the fetal central nervous system: guidelines for performing the 'basic examination' and the 'fetal neurosonogram'. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 2007;29(1):109–16. PubMed PMID: 17200992.
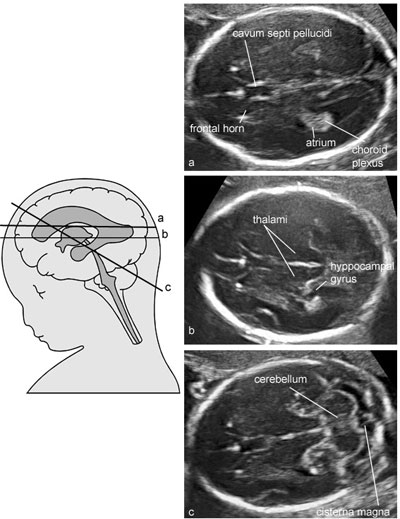
Normal fetal brain at midgestation: advanced examination
Legend:Normal fetal brain at midgestation: advanced examination
Reference(s):International Society of Ultrasound in Obstetrics & Gynecology Education Committee. Sonographic examination of the fetal central nervous system: guidelines for performing the 'basic examination' and the 'fetal neurosonogram'. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 2007;29(1):109–16. PubMed PMID: 17200992.
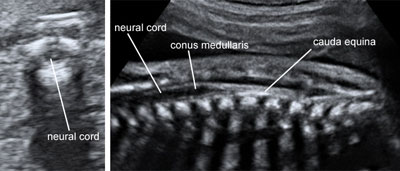
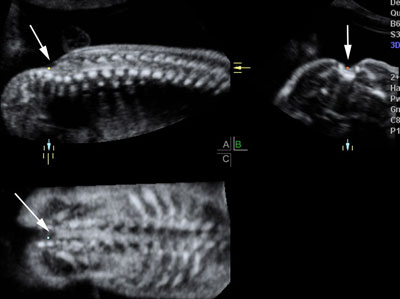
Fetal spine and neural canal
Legend:Fetal spine and neural canal
Reference(s):International Society of Ultrasound in Obstetrics & Gynecology Education Committee. Sonographic examination of the fetal central nervous system: guidelines for performing the 'basic examination' and the 'fetal neurosonogram'. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 2007;29(1):109–16. PubMed PMID: 17200992.
Cerebral vessels
Legend:Cerebral vessels
Reference(s):Ebbing C, Rasmussen S, Kiserud T. Middle cerebral artery blood flow velocities and pulsatility index and the cerebroplacental pulsatility ratio: longitudinal reference ranges and terms for serial measurements. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 2007;30(3):287–96. PubMed PMID: 17721916. Jugovic D, Tumbri J, Medi? M, Juki? MK, Kurjak A, Arbeille P, Salihagic-Kadic A. New Doppler index for prediction of perinatal brain damage in growth-restricted and hypoxic fetuses. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 2007;30(3):303–11. PubMed PMID: 17721870. Figueroa-Diesel H, Hernandez-Andrade E, Acosta-Rojas R, Cabero L, Gratacos E. Doppler changes in the main fetal brain arteries at different stages of hemodynamic adaptation in severe intrauterine growth restriction. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 2007;30(3):297–302. PubMed PMID: 17661428. Mari G, Hanif F, Kruger M, Cosmi E, Santolaya-Forgas J, Treadwell MC. Middle cerebral artery peak systolic velocity: a new Doppler parameter in the assessment of growth-restricted fetuses. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 2007;29(3):310–6. PubMed PMID: 17318946. Figueras F, Fernandez S, Eixarch E, Gomez O, Martinez JM, Puerto B, Gratacos E. Middle cerebral artery pulsatility index: reliability at different sampling sites. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol. 2006 Nov;28(6):809–13. PubMed PMID: 17019746. Laurichesse-Delmas H, Grimaud O, Moscoso G, Ville Y. Color Doppler study of the venous circulation in the fetal brain and hemodynamic study of the cerebral transverse sinus. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 1999;13(1):34–42. PubMed PMID: 10201084. Mari G, Adrignolo A, Abuhamad AZ, Pirhonen J, Jones DC, Ludomirsky A, Copel JA. Diagnosis of fetal anemia with Doppler ultrasound in the pregnancy complicated by maternal blood group immunization. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 1995;5(6):400–5. PubMed PMID: 7552802. Degani S, Lewinsky RM, Shapiro I. Doppler studies of fetal cerebral blood flow. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 1994;4(2):158–65. PubMed PMID: 12797213.
Anencephaly throughout gestation
Legend:Anencephaly throughout gestation
Reference(s):Becker R, Mende B, Stiemer B, Entezami M. Sonographic markers of exencephaly at 9 + 3 weeks of gestation. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 2000;16(6):582–4.PubMed PMID: 11169357. Chatzipapas IK, Whitlow BJ, Economides DL. The 'Mickey Mouse' sign and the diagnosis of anencephaly in early pregnancy. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 1999;13(3):196–9. PubMed PMID: 10204212. Johnson SP, Sebire NJ, Snijders RJ, Tunkel S, Nicolaides KH. Ultrasound screening for anencephaly at 10-14 weeks of gestation. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 1997;9(1):14–6. PubMed PMID: 9060123. Salamanca A, Gonzalez-Gomez F, Padilla MC, Sabatel RM, Cámara M, Cuadros JL. Prenatal ultrasound semiography of anencephaly: sonographic-pathological correlations. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 1992;2(2):95–100. PubMed PMID: 12796984.
Cephaloceles
Legend:Cephaloceles
Reference(s):Sepulveda W, Corral E, Ayala C, Be C, Gutierrez J, Vasquez P. Chromosomal abnormalities in fetuses with open neural tube defects: prenatal identification with ultrasound. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 2004;23(4):352–6. PubMed PMID: 15065184. Budorick NE, Pretorius DH, McGahan JP, Grafe MR, James HE, Slivka J. Cephalocele detection in utero: sonographic and clinical features. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 1995;5(2):77–85. PubMed PMID: 7719871. van Zalen-Sprock MM, van Vugt JM, van dHarten HJ, van Geijn HP. Cephalocele and cystic hygroma: diagnosis and differentiation in the first trimester of pregnancy with transvaginal sonography. Report of two cases. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 1992;2(4):289–92. PubMed PMID: 12796957.
Myelomeningocele
Legend:Myelomeningocele
Reference(s):Ghi T, Pilu G, Falco P, Segata M, Carletti A, Cocchi G, Santini D, Bonasoni P, Tani G, Rizzo N. Prenatal diagnosis of open and closed spina bifida. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 2006;28(7):899–903. PubMed PMID: 17086581.
Myelocele
Legend:Myelocele
Reference(s):Ghi T, Pilu G, Falco P, Segata M, Carletti A, Cocchi G, Santini D, Bonasoni P, Tani G, Rizzo N. Prenatal diagnosis of open and closed spina bifida. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 2006;28(7):899–903. PubMed PMID: 17086581.
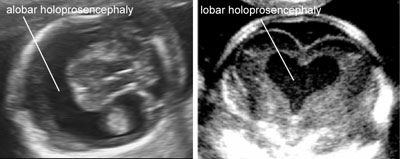
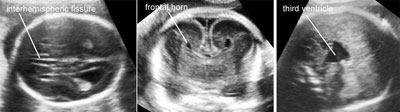
Holoprosencephaly
Legend:Holoprosencephaly
Reference(s):Timor-Tritsch IE, Monteagudo A, Santos R. Three-dimensional inversion rendering in the first- and early second-trimester fetal brain: its use in holoprosencephaly. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 2008;32(6):744–50. PubMed PMID: 18956427. Picone O, Hirt R, Suarez B, Coulomb A, Tachdjian G, Frydman R, Senat MV. Prenatal diagnosis of a possible new middle interhemispheric variant of holoprosencephaly using sonographic and magnetic resonance imaging. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 2006;28(2):229–31. PubMed PMID: 16933282. Malinger G, Lev D, Kidron D, Heredia F, Hershkovitz R, Lerman-Sagie T. Differential diagnosis in fetuses with absent septum pellucidum. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 2005;25(1):42–9. PubMed PMID: 15593321. Blin G, Rabbé A, Mandelbrot L. Prenatal diagnosis of lobar holoprosencephaly using color Doppler: three cases with the anterior cerebral artery crawling under the skull. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 2004;24(4):476–8. PubMed PMID: 15343609. Bernard JP, Drummond CL, Zaarour P, Molho M, Ville Y. A new clue to the prenatal diagnosis of lobar holoprosencephaly: the abnormal pathway of the anterior cerebral artery crawling under the skull. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 2002;19(6):605–7. PubMed PMID: 12099261. Blaas HG, Eriksson AG, Salvesen KA, Isaksen CV, Christensen B, Møllerløkken G, Eik-Nes SH. Brains and faces in holoprosencephaly: pre- and postnatal description of 30 cases. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 2002;19(1):24-38. PubMed PMID: 11851965. Blaas HG. Holoprosencephaly at 10 weeks 2 days (CRL 33 mm). Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 2000;15(1):86–7. PubMed PMID: 10776022. Pilu G, Ambrosetto P, Sandri F, Tani G, Perolo A, Grisolia G, Ancora G. Intraventricular fused fornices: a specific sign of fetal labor holoprosencephaly. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 1994;4(1):65-7. PubMed PMID: 12797228. Pilu G, Sandri F, Perolo A, Giangaspero F, Cocchi G, Salvioli GP, Bovicelli L. Prenatal diagnosis of lobar holoprosencephaly. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 1992;2(2):88–94. PubMed PMID: 12796983.
Facial anomalies with holoprosencephaly
Legend:Facial anomalies with holoprosencephaly
Reference(s):Blaas HG, Eriksson AG, Salvesen KA, Isaksen CV, Christensen B, Møllerløkken G, Eik-Nes SH. Brains and faces in holoprosencephaly: pre- and postnatal description of 30 cases. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 2002;19(1):24–38. PubMed PMID: 11851965. Blaas HG. Holoprosencephaly at 10 weeks 2 days (CRL 33 mm). Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 2000;15(1):86–7. PubMed PMID: 10776022. Blaas HG, Eik-Nes SH, Vainio T, Isaksen CV. Alobar holoprosencephaly at 9 weeks gestational age visualized by two- and three-dimensional ultrasound. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 2000;15(1):62–5. PubMed PMID: 10776015.
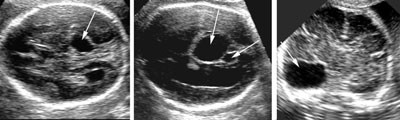
Agenesis of the septum pellucidum
Legend:With agenesis of the septum pellucidum there is a central communication between the cavities of the frontal horns
Reference(s):Pilu G, Tani G, Carletti A, Malaigia S, Ghi T, Rizzo N. Difficult early sonographic diagnosis of absence of the fetal septum pellucidum. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 2005;25(1):70–2. PubMed PMID: 15619322. Malinger G, Lev D, Kidron D, Heredia F, Hershkovitz R, Lerman-Sagie T. Differential diagnosis in fetuses with absent septum pellucidum. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 2005;25(1):42–9. PubMed PMID: 15593321. Lepinard C, Coutant R, Boussion F, Loisel D, Delorme B, Biquard F, Bonneau D, Guichet A, Descamps P. Prenatal diagnosis of absence of the septum pellucidum associated with septo-optic dysplasia. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 2005;25(1):73–5. PubMed PMID: 15593257. Falco P, Gabrielli S, Visentin A, Perolo A, Pilu G, Bovicelli L. Transabdominal sonography of the cavum septum pellucidum in normal fetuses in the second and third trimesters of pregnancy. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 2000;16(6):549–53. PubMed PMID: 11169349.
Complete agenesis of the corpus callosum
Legend:Complete agenesis of the corpus callosum: in most fetuses with complete agenesis of the corpus callosum there is a wide interhemispheric fissure and lateral separation of frontal horns
Reference(s):Pilu G, Segata M, Ghi T, Carletti A, Perolo A, Santini D, Bonasoni P, Tani G, Rizzo N. Diagnosis of midline anomalies of the fetal brain with the three-dimensional median view. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 2006;27(5):522–9. PubMed PMID: 16586477. Malinger G, Lev D, Kidron D, Heredia F, Hershkovitz R, Lerman-Sagie T. Differential diagnosis in fetuses with absent septum pellucidum. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 2005;25(1):42–9. PubMed PMID: 15593321. Pilu G, Sandri F, Perolo A, Pittalis MC, Grisolia G, Cocchi G, Foschini MP, Salvioli GP, Bovicelli L. Sonography of fetal agenesis of the corpus callosum: a survey of 35 cases. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 1993;3(5):318–29. PubMed PMID: 12797254.
Partial agenesis of the corpus callosum
Legend:With partial agenesis of the corpus callosum only the most anterior portion is present
Reference(s):Pilu G, Segata M, Ghi T, Carletti A, Perolo A, Santini D, Bonasoni P, Tani G, Rizzo N. Diagnosis of midline anomalies of the fetal brain with the three-dimensional median view. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 2006;27(5):522–9. PubMed PMID: 16586477. Volpe P, Paladini D, Resta M, Stanziano A, Salvatore M, Quarantelli M, De Robertis V, Buonadonna AL, Caruso G, Gentile M. Characteristics, associations and outcome of partial agenesis of the corpus callosum in the fetus. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 2006;27(5):509–16. PubMed PMID: 16619387. Pilu G, Sandri F, Perolo A, Pittalis MC, Grisolia G, Cocchi G, Foschini MP, Salvioli GP, Bovicelli L. Sonography of fetal agenesis of the corpus callosum: a survey of 35 cases. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 1993;3(5):318–29. PubMed PMID: 12797254.
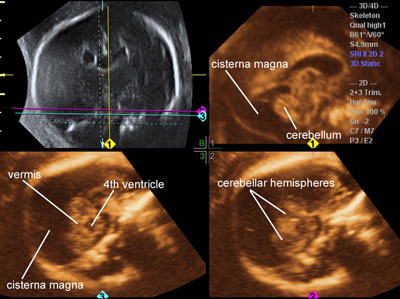
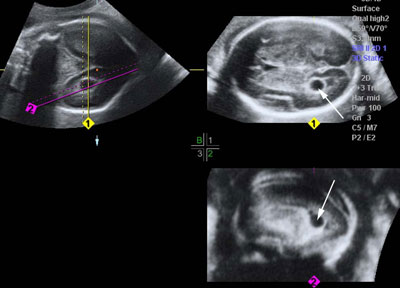
Megacisterna magna
Legend:With megacisterna magna the depth of the cisterna magna is increased but the cerebellum has a normal appearance and the fourth ventricle appears normally closed by the posterior vermis
Reference(s):Pilu G, Segata M, Ghi T, Carletti A, Perolo A, Santini D, Bonasoni P, Tani G, Rizzo N. Diagnosis of midline anomalies of the fetal brain with the three-dimensional median view. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 2006;27(5):522–9. PubMed PMID: 16586477. Guibaud L, des Portes V. Plea for an anatomical approach to abnormalities of the posterior fossa in prenatal diagnosis. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 2006;27(5):477–81. PubMed PMID: 16619384. Paladini D, Volpe P. Posterior fossa and vermian morphometry in the characterization of fetal cerebellar abnormalities: a prospective three-dimensional ultrasound study. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 2006;27(5):482–9. PubMed PMID: 16619375. Pilu G, Visentin A, Valeri B. The Dandy-Walker complex and fetal sonography. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 2000;16(2):115–7. Review. PubMed PMID: 11117078.
Dandy-Walker malformation
Legend:Dandy-Walker malformation is a distortion of the anatomy of the posterior fossa characterized by the following elements: the cisterna magna is expanded and the tentorium is displaced superiorly, the cerebellar vermis is rotated superiorly and this results in a posterior opening of the fourth ventricle; the vermis may be normal, hypoplastic or absent; the cerebellar hemispheres may be normal or hypoplastic; ventriculomegaly and other anomalies are frequent
Reference(s):Pilu G, Segata M, Ghi T, Carletti A, Perolo A, Santini D, Bonasoni P, Tani G, Rizzo N. Diagnosis of midline anomalies of the fetal brain with the three-dimensional median view. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 2006;27(5):522–9. PubMed PMID: 16586477. Guibaud L, des Portes V. Plea for an anatomical approach to abnormalities of the posterior fossa in prenatal diagnosis. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 2006;27(5):477–81. PubMed PMID: 16619384. Paladini D, Volpe P. Posterior fossa and vermian morphometry in the characterization of fetal cerebellar abnormalities: a prospective three-dimensional ultrasound study. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 2006;27(5):482–9. PubMed PMID: 16619375. Pilu G, Visentin A, Valeri B. The Dandy-Walker complex and fetal sonography. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 2000;16(2):115–7. Review. PubMed PMID: 11117078.
Blake’s pouch cyst
Legend:This anomaly is similar to the Dandy-Walker malformation but for the tentorium that is in a normal position and the vermis that is by definition intact; frequently it is a normal variant without clinical implications
Reference(s):Zalel Y, Gilboa Y, Gabis L, Ben-Sira L, Hoffman C, Wiener Y, Achiron R. Rotation of the vermis as a cause of enlarged cisterna magna on prenatal imaging. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 2006;27(5):490–3. PubMed PMID: 16619381. Pilu G, Segata M, Ghi T, Carletti A, Perolo A, Santini D, Bonasoni P, Tani G, Rizzo N. Diagnosis of midline anomalies of the fetal brain with the three-dimensional median view. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 2006;27(5):522–9. PubMed PMID: 16586477. Guibaud L, des Portes V. Plea for an anatomical approach to abnormalities of the posterior fossa in prenatal diagnosis. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 2006;27(5):477–81. PubMed PMID: 16619384. Paladini D, Volpe P. Posterior fossa and vermian morphometry in the characterization of fetal cerebellar abnormalities: a prospective three-dimensional ultrasound study. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 2006;27(5):482–9. PubMed PMID: 16619375. Pilu G, Visentin A, Valeri B. The Dandy-Walker complex and fetal sonography. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 2000;16(2):115–7. Review. PubMed PMID: 11117078.
Vermian hypoplasia
Legend:This anomaly is similar to Blake’s pouch cyst but for the hypoplasia of the vermis that is small and dysmorphic. It was once referred to as ‘Dandy-Walker variant’ and is frequently associated with other anomalies
Reference(s):Pilu G, Segata M, Ghi T, Carletti A, Perolo A, Santini D, Bonasoni P, Tani G, Rizzo N. Diagnosis of midline anomalies of the fetal brain with the three-dimensional median view. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 2006;27(5):522–9. PubMed PMID: 16586477. Guibaud L, des Portes V. Plea for an anatomical approach to abnormalities of the posterior fossa in prenatal diagnosis. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 2006;27(5):477–81. PubMed PMID: 16619384. Paladini D, Volpe P. Posterior fossa and vermian morphometry in the characterization of fetal cerebellar abnormalities: a prospective three-dimensional ultrasound study. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 2006;27(5):482–9. PubMed PMID: 16619375. Pilu G, Visentin A, Valeri B. The Dandy-Walker complex and fetal sonography. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 2000;16(2):115–7. Review. PubMed PMID: 11117078.
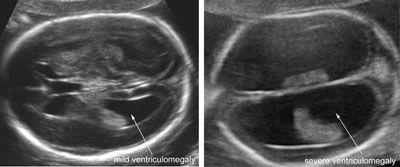
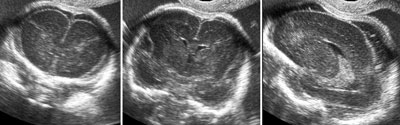
Cerebral lateral ventriculomegaly
Legend:Cerebral lateral ventriculomegaly
Reference(s):Guibaud L. Fetal cerebral ventricular measurement and ventriculomegaly: time for procedure standardization. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 2009;34(2):127–30. PubMed PMID: 19644945. Melchiorre K, Bhide A, Gika AD, Pilu G, Papageorghiou AT. Counseling in isolated mild fetal ventriculomegaly. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 2009;34(2):212–24. PubMed PMID: 19644944. Gaglioti P, Danelon D, Bontempo S, Mombrò M, Cardaropoli S, Todros T. Fetal cerebral ventriculomegaly: outcome in 176 cases. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 2005;25(4):372–7. PubMed PMID: 15791694. Signorelli M, Tiberti A, Valseriati D, Molin E, Cerri V, Groli C, Bianchi UA. Width of the fetal lateral ventricular atrium between 10 and 12 mm: a simple variation of the norm? Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 2004;23(1):14–8. PubMed PMID: 14970992.
Types of cerebral lateral ventriculomegaly
Legend:Types of cerebral lateral ventriculomegaly
Reference(s):Guibaud L. Fetal cerebral ventricular measurement and ventriculomegaly: time for procedure standardization. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 2009;34(2):127–30. PubMed PMID: 19644945. Melchiorre K, Bhide A, Gika AD, Pilu G, Papageorghiou AT. Counseling in isolated mild fetal ventriculomegaly. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 2009;34(2):212–24. PubMed PMID: 19644944. Gaglioti P, Danelon D, Bontempo S, Mombrò M, Cardaropoli S, Todros T. Fetal cerebral ventriculomegaly: outcome in 176 cases. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 2005;25(4):372–7. PubMed PMID: 15791694. Signorelli M, Tiberti A, Valseriati D, Molin E, Cerri V, Groli C, Bianchi UA. Width of the fetal lateral ventricular atrium between 10 and 12 mm: a simple variation of the norm? Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 2004;23(1):14–8. PubMed PMID: 14970992.
Intracranial hemorrhage
Legend:A large blood clot within the distended lateral ventricles and a cystic cavity in the periventricular cortex suggestive of a parenchymal infarction: this is a grade IV hemorrhage
Reference(s):Elchalal U, Yagel S, Gomori JM, Porat S, Beni-Adani L, Yanai N, Nadjari M. Fetal intracranial hemorrhage (fetal stroke): does grade matter? Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 2005;26(3):233–43. PubMed PMID: 16082722. Ghi T, Simonazzi G, Perolo A, Savelli L, Sandri F, Bernardi B, Santini D, Bovicelli L, Pilu G. Outcome of antenatally diagnosed intracranial hemorrhage: case series and review of the literature. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 2003;22(2):121–30. Review. PubMed PMID: 12905503. Yüksel A, Batukan C. Fetal cerebellar hemorrhage in a severely growth-restricted fetus: natural history and differential diagnosis from Dandy-Walker malformation. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 2003;22(2):178–81. PubMed PMID: 12905514.
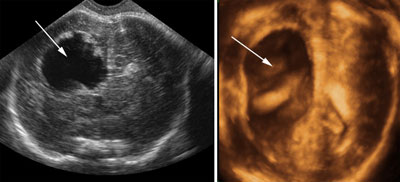
Porencephalic cyst
Legend:Porencephalic cyst
Reference(s):Simonazzi G, Segata M, Ghi T, Sandri F, Ancora G, Bernardi B, Tani G, Rizzo N, Santini D, Bonasoni P, Pilu G. Accurate neurosonographic prediction of brain injury in the surviving fetus after the death of a monochorionic cotwin. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 2006;27(5):517–21. PubMed PMID: 16586472. Elchalal U, Yagel S, Gomori JM, Porat S, Beni-Adani L, Yanai N, Nadjari M. Fetal intracranial hemorrhage (fetal stroke): does grade matter? Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 2005;26(3):233–43. PubMed PMID: 16082722. Ghi T, Simonazzi G, Perolo A, Savelli L, Sandri F, Bernardi B, Santini D, Bovicelli L, Pilu G. Outcome of antenatally diagnosed intracranial hemorrhage: case series and review of the literature. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 2003;22(2):121–30. Review. PubMed PMID: 12905503. Pilu G, Falco P, Perolo A, Sandri F, Cocchi G, Ancora G, Bovicelli L. Differential diagnosis and outcome of fetal intracranial hypoechoic lesions: report of 21 cases. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 1997;9(4):229–36. PubMed PMID: 9168572.
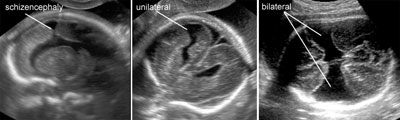
Schizencephaly: unilateral and bilateral
Legend:Schizencephaly: unilateral and bilateral
Reference(s):Malinger G, Kidron D, Schreiber L, Ben-Sira L, Hoffmann C, Lev D, Lerman-Sagie T. Prenatal diagnosis of malformations of cortical development by dedicated neurosonography. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 2007;29(2):178–91. PubMed PMID: 17219377. Pilu G, Falco P, Perolo A, Sandri F, Cocchi G, Ancora G, Bovicelli L. Differential diagnosis and outcome of fetal intracranial hypoechoic lesions: report of 21 cases. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 1997;9(4):229–36. PubMed PMID: 9168572.
Periventricular leukomalacia
Legend:The cortex in the periventricular area appears inhomogeneous, hyperechogenic with multiple microcysts
Reference(s):Ghi T, Brondelli L, Simonazzi G, Valeri B, Santini D, Sandri F, Ancora G, Pilu G. Sonographic demonstration of brain injury in fetuses with severe red blood cell alloimmunization undergoing intrauterine transfusions. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 2004;23(5):428–31. PubMed PMID: 15133789. van Gelder-Hasker MR, van Wezel-Meijler G, de Groot L, van Geijn HP, de Vries JI. Peri- and intraventricular cerebral sonography in second- and third-trimester high-risk fetuses: a comparison with neonatal ultrasound and relation to neurological development. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 2003;22(2):110–20. PubMed PMID: 12905502. Pilu G, Falco P, Perolo A, Sandri F, Cocchi G, Ancora G, Bovicelli L. Differential diagnosis and outcome of fetal intracranial hypoechoic lesions: report of 21 cases. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 1997;9(4):229–36. PubMed PMID: 9168572.
Brain findings with fetal cytomegalovirus infection
Legend:(a) and (b) Periventricular echogenic halo similar to that described for periventricular leukomalacia, mild ventriculomegaly, irregular choroid plexus; (c) a more severe case; echogenicities within the cortex are associated with an excessive size of the subarachnoid space suggesting microencephaly.
Reference(s):Benoist G, Salomon LJ, Mohlo M, Suarez B, Jacquemard F, Ville Y. Cytomegalovirus-related fetal brain lesions: comparison between targeted ultrasound examination and magnetic resonance imaging. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 2008;32(7):900–5. PubMed PMID: 18991327. Malinger G, Ben-Sira L, Lev D, Ben-Aroya Z, Kidron D, Lerman-Sagie T. Fetal brain imaging: a comparison between magnetic resonance imaging and dedicated neurosonography. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 2004;23(4):333–40. PubMed PMID: 15065181. Malinger G, Lev D, Ben Sira L, Kidron D, Tamarkin M, Lerman-Sagie T. Congenital periventricular pseudocysts: prenatal sonographic appearance and clinical implications. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 2002;20(5):447–51. PubMed PMID: 12423480. Ville Y. The megalovirus. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 1998;12(3):151–3. Review. PubMed PMID: 9793184.
Brain findings with fetal toxoplasmosis
Legend:Mild ventriculomegaly, multiple echogenicities into the cortex
Reference(s):Hohlfeld P, MacAleese J, Capella-Pavlovski M, Giovangrandi Y, Thulliez P, Forestier F, Daffos F. Fetal toxoplasmosis: ultrasonographic signs. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 1991;1(4):241–4. PubMed PMID: 12797051. Holliman RE. Toxoplasmosis and pregnancy. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 1991;1(4):234. PubMed PMID: 12797049. Pedreira DA, Camargo ME, Leser PG. Toxoplasmosis: will the time ever come? Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 2001;17(6):459–63. PubMed PMID: 11422964.
Intracranial arachnoid cysts
Legend:Intracranial arachnoid cysts
Reference(s):Bretelle F, Senat MV, Bernard JP, Hillion Y, Ville Y. First-trimester diagnosis of fetal arachnoid cyst: prenatal implication. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 2002;20(4):400–2. PubMed PMID: 12383327. Campbell S, Chudleigh T. Picture of the month. Diagnosis of arachnoid cysts. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 1999;14(5):365-6. PubMed PMID: 10624002. Pilu G, Falco P, Perolo A, Sandri F, Cocchi G, Ancora G, Bovicelli L. Differential diagnosis and outcome of fetal intracranial hypoechoic lesions: report of 21 cases. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 1997;9(4):229–36. PubMed PMID: 9168572. Langer B, Haddad J, Favre R, Frigue V, Schlaeder G. Fetal arachnoid cyst: report of two cases. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 1994;4(1):68–72. PubMed PMID: 12797229.
Choroid plexus cyst
Legend:Choroid plexus cyst
Reference(s):Bottalico JN, Chen X, Tartaglia M, Rosario B, Yarabothu D, Nelson L. Second-trimester genetic sonogram for detection of fetal chromosomal abnormalities in a community-based antenatal testing unit. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 2009;33(2):161–8. PubMed PMID: 19173242. Dagklis T, Plasencia W, Maiz N, Duarte L, Nicolaides KH. Choroid plexus cyst, intracardiac echogenic focus, hyperechogenic bowel and hydronephrosis in screening for trisomy 21 at 11 + 0 to 13 + 6 weeks. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 2008;31(2):132–5. PubMed PMID: 18085527. Chitty LS, Chudleigh P, Wright E, Campbell S, Pembrey M. The significance of choroid plexus cysts in an unselected population: results of a multicenter study. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 1998;12(6):391–7. PubMed PMID: 9918087. Geary M, Patel S, Lamont R. Isolated choroid plexus cysts and association with fetal aneuploidy in an unselected population. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 1997;10(3):171–3. PubMed PMID: 9339524. Donnenfeld AE. Risk and benefit analysis of offering karyotyping for an isolated choroid plexus cyst. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 1997;9(1):67–8. PubMed PMID: 9060136. Bromley B, Lieberman R, Benacerraf BR. Choroid plexus cysts: not associated with Down syndrome. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 1996;8(4):232–5. PubMed PMID: 8916374. Snijders RJ. Isolated choroid plexus cysts: should we offer karyotyping? Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 1996;8(4):223–4. Review. PubMed PMID: 8916371.
Vein of Galen aneurysm
Legend:Vein of Galen aneurysm
Reference(s):Garel C, Azarian M, Lasjaunias P, Luton D. Pial arteriovenous fistulas: dilemmas in prenatal diagnosis, counseling and postnatal treatment. Report of three cases. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 2005;26(3):293–6. PubMed PMID: 16052602. Heling KS, Chaoui R, Bollmann R. Prenatal depiction of the angioarchitecture of an aneurysm of the vein of Galen with three-dimensional color power angiography. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 2000;15(4):345. Erratum in: Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 2000 May;15(5):449. PubMed PMID: 10895461. Bahlmann F. Three-dimensional color power angiography of an aneurysm of the vein of Galen. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 2000;15(4):341. PubMed PMID: 10895458. Lee TH, Shih JC, Peng SS, Lee CN, Shyu MK, Hsieh FJ. Prenatal depiction of angioarchitecture of an aneurysm of the vein of Galen with three-dimensional color power angiography. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 2000;15(4):337–40. PubMed PMID: 10895457. Heling KS, Chaoui R, Bollmann R. Prenatal diagnosis of an aneurysm of the vein of Galen with three-dimensional color power angiography. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 2000;15(4):333–6. PubMed PMID: 10895456. Sepulveda W, Platt CC, Fisk NM. Prenatal diagnosis of cerebral arteriovenous malformation using color Doppler ultrasonography: case report and review of the literature. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 1995;6(4):282–6. Review. PubMed PMID: 8590192.
Lissencephaly
Legend:The surface of the brain is unusually smooth for a fetus at 28 weeks’ gestation (the Sylvian fossa is shallow and there is no sign of the cingulate and precentral gyrus; the texture of the cortex is more irregular and echogenic than usual
Reference(s):Malinger G, Kidron D, Schreiber L, Ben-Sira L, Hoffmann C, Lev D, Lerman-Sagie T. Prenatal diagnosis of malformations of cortical development by dedicated neurosonography. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 2007;29(2):178–91. PubMed PMID: 17219377.
Unilateral megalencephaly
Legend:Overgrowth of one hemisphere that appears brightly echogenic with a lateral ventricle irregularly enlarged
Reference(s):Malinger G, Kidron D, Schreiber L, Ben-Sira L, Hoffmann C, Lev D, Lerman-Sagie T. Prenatal diagnosis of malformations of cortical development by dedicated neurosonography. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 2007;29(2):178–91. PubMed PMID: 17219377.
Intracranial tumors
Legend:Teratoma results in complex masses that cannot be clearly differentiated from the surrounding normal brain tissue; craniopharyngioma is a well defined echogenic mass
Reference(s):Kamil D, Tepelmann J, Berg C, Heep A, Axt-Fliedner R, Gembruch U, Geipel A. Spectrum and outcome of prenatally diagnosed fetal tumors. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 2008;31(3):296–302. PubMed PMID: 18307207. Müller T, Girschick G, Mark K, Wirbelauer J, Klein R, Collmann H, Dietl J. Fetal intracranial tumors detected by ultrasound. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 2001;18(3):290–1. PubMed PMID: 11555465. Schlembach D, Bornemann A, Rupprecht T, Beinder E. Fetal intracranial tumors detected by ultrasound: a report of two cases and review of the literature. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 1999;14(6):407–18. Review. PubMed PMID: 10658280.
The fetal heart
Normal fetus situs
Legend:Normal fetus situs
Reference(s):Yagel S, Cohen SM, Achiron R. Examination of the fetal heart by five short-axis views: a roposed screening method for comprehensive cardiac evaluation. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 2001;17(5):367–9. PubMed PMID: 11380958. International Society of Ultrasound in Obstetrics & Gynecology. Cardiac screening examination of the fetus: guidelines for performing the 'basic' and 'extended basic' cardiac scan. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 2006;27(1):107–13. PubMed PMID: 16374757. Lee W, Allan L, Carvalho JS, Chaoui R, Copel J, Devore G, Hecher K, Munoz H, Nelson T, Paladini D, Yagel S; ISUOG Fetal Echocardiography Task Force. ISUOG consensus statement: what constitutes a fetal echocardiogram? Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 2008;32(2):239–42. PubMed PMID: 18663769.
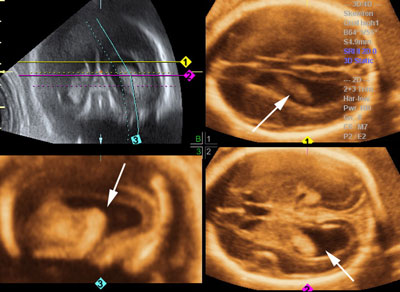
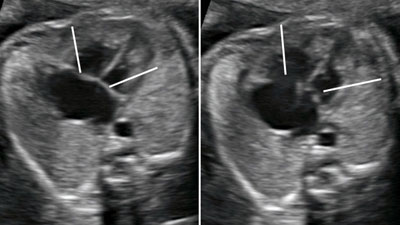
Two-dimensional gray scale imaging of fetal cardiac connections
Legend:Two-dimensional gray scale imaging of fetal cardiac connections
Reference(s):Yagel S, Cohen SM, Achiron R. Examination of the fetal heart by five short-axis views: a proposed screening method for comprehensive cardiac evaluation. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 2001;17(5):367–9. PubMed PMID: 11380958. International Society of Ultrasound in Obstetrics & Gynecology. Cardiac screening examination of the fetus: guidelines for performing the 'basic' and 'extended basic' cardiac scan. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 2006;27(1):107–13. PubMed PMID: 16374757.
Color Doppler of fetal cardiac connections
Legend:Color Doppler of fetal cardiac connections
Reference(s):Chaoui R, McEwing R. Three cross-sectional planes for fetal color Doppler echocardiography. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 2003;21(1):81–93. Review. PubMed PMID: 12528169. Lee W, Allan L, Carvalho JS, Chaoui R, Copel J, Devore G, Hecher K, Munoz H, Nelson T, Paladini D, Yagel S; ISUOG Fetal Echocardiography Task Force. ISUOG consensus statement: what constitutes a fetal echocardiogram? Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 2008;32(2):239–42. PubMed PMID: 18663769. Chaoui R. Fetal echocardiography: state of the art of the state of the heart. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 2001;17(4):277–84. Review. PubMed PMID: 11339181.
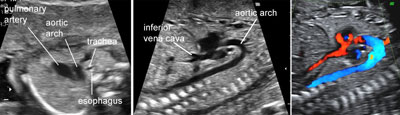
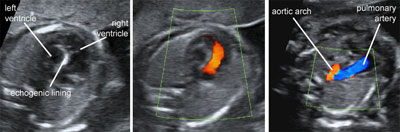
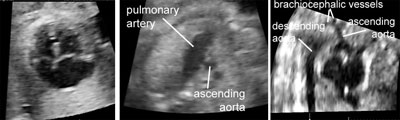
The fetal aortic arch
Legend:The fetal aortic arch
High definition flow of the fetal aortic arch
Legend:High definition flow of the fetal aortic arch
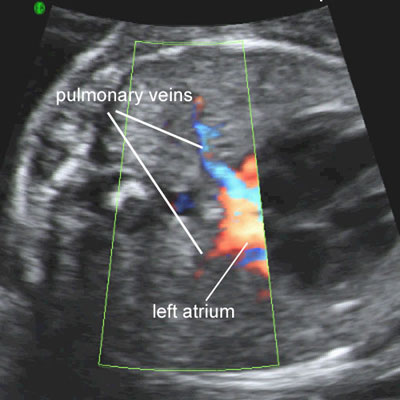
Color Doppler of pulmonary veins
Legend:Color Doppler of pulmonary veins
Three-dimensional ultrasound of normal fetal heart
Legend:Three-dimensional ultrasound of normal fetal heart
Reference(s):Yagel S, Cohen SM, Shapiro I, Valsky DV. 3D and 4D ultrasound in fetal cardiac scanning: a new look at the fetal heart. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 2007;29(1):81–95. Review. PubMed PMID: 17200988. Espinoza J, Romero R, Kusanovic JP, Gotsch F, Lee W, Gonçalves LF, Hassan SS. Standardized views of the fetal heart using four-dimensional sonographic and tomographic imaging. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 2008;31(2):233–42. PubMed PMID: 18254137; PubMed Central PMCID: PMC2361149. Gonçalves LF, Lee W, Espinoza J, Romero R. Examination of the fetal heart by four-dimensional (4D) ultrasound with spatio-temporal image correlation (STIC). Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 2006;27(3):336–48. Review. PubMed PMID: 16482611.
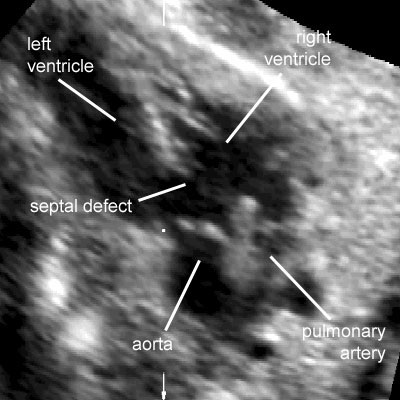
Two-dimensional gray scale imaging of ventricular septal defects
Legend:Two-dimensional gray scale imaging of ventricular septal defects
Reference(s):Paladini D, Palmieri S, Lamberti A, Teodoro A, Martinelli P, Nappi C. Characterization and natural history of ventricular septal defects in the fetus. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 2000;16(2):118–22. PubMed PMID: 11117079.
Color and pulsed Doppler of blood shunting across a muscular ventricular septal defect
Legend:Color and pulsed Doppler of blood shunting across a muscular ventricular septal defect
Reference(s):Paladini D, Palmieri S, Lamberti A, Teodoro A, Martinelli P, Nappi C. Characterization and natural history of ventricular septal defects in the fetus. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 2000;16(2):118–22. PubMed PMID: 11117079. Axt-Fliedner R, Schwarze A, Smrcek J, Germer U, Krapp M, Gembruch U. Isolated ventricular septal defects detected by color Doppler imaging: evolution during fetal and first year of postnatal life. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 2006;27(3):266–73. PubMed PMID: 16485323.
Muscular ventricular septal defect
Legend:Muscular ventricular septal defect
Reference(s):Paladini D, Palmieri S, Lamberti A, Teodoro A, Martinelli P, Nappi C. Characterization and natural history of ventricular septal defects in the fetus. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 2000;16(2):118–22. PubMed PMID: 11117079.
Inlet ventricular septal defect
Legend:Inlet ventricular septal defect
Reference(s):Paladini D, Palmieri S, Lamberti A, Teodoro A, Martinelli P, Nappi C. Characterization and natural history of ventricular septal defects in the fetus. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 2000;16(2):118–22. PubMed PMID: 11117079.
Outlet ventricular septal defect
Legend:Outlet ventricular septal defect: the arrow indicates a large defect of the outlet portion of the ventricular septum associated with malalignment of the great vessels
Reference(s):Paladini D, Palmieri S, Lamberti A, Teodoro A, Martinelli P, Nappi C. Characterization and natural history of ventricular septal defects in the fetus. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 2000;16(2):118–22. PubMed PMID: 11117079.
Perimembranous ventricular septal defect
Legend:Perimembranous ventricular septal defect
Reference(s):Paladini D, Palmieri S, Lamberti A, Teodoro A, Martinelli P, Nappi C. Characterization and natural history of ventricular septal defects in the fetus. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 2000;16(2):118–22. PubMed PMID: 11117079.
Apical ventricular septal defect
Legend:Apical ventricular septal defect
Reference(s):Paladini D, Palmieri S, Lamberti A, Teodoro A, Martinelli P, Nappi C. Characterization and natural history of ventricular septal defects in the fetus. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 2000;16(2):118–22. PubMed PMID: 11117079.
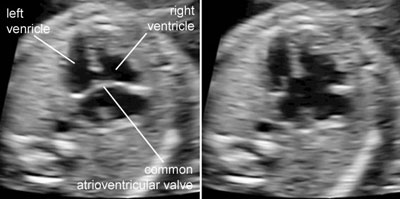
Complete atrioventricular canal
Legend:Complete atrioventricular canal
Reference(s):Machlitt A, Heling KS, Chaoui R. Increased cardiac atrial-to-ventricular length ratio in the fetal four-chamber view: a new marker for atrioventricular septal defects. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 2004;24(6):618–22. PubMed PMID: 15517546.
Partial atrioventricular canal
Legend:Partial atrioventricular canal: two separate atrioventricular valves insert at the same level on the ventricular septum, and there is a defect of the atrial septum primum
Reference(s):Paladini D, Volpe P, Sglavo G, Russo MG, De Robertis V, Penner I, Nappi C. Partial atrioventricular septal defect in the fetus: diagnostic features and associations in a multicenter series of 30 cases. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 2009;34(3):268–73. PubMed PMID: 19705406.
Single ventricles
Legend:Types of single ventricles: atresia of the tricuspid valve and double inlet single ventricle
Hypoplastic left heart syndrome
Legend:Hypoplastic left heart syndrome: there is a small left ventricle with an internal echogenic lining suggestive of endocardial fibroelastosis, there is no flow across the mitral valve and the aortic arch is perfused in a retrograde manner
Reference(s):Simpson JM. Hypoplastic left heart syndrome. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 2000;15(4):271–8. Review. PubMed PMID: 10895443. Galindo A, Nieto O, Villagrá S, Grañeras A, Herraiz I, Mendoza A. Hypoplastic left heart syndrome diagnosed in fetal life: associated findings, pregnancy outcome and results of palliative surgery. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 2009;33(5):560–6. PubMed PMID: 19367583.
Pulmonary atresia with intact ventricular septum
Legend:Pulmonary atresia with intact ventricular septum: the right ventricle is small, there is significant tricuspid regurgitation, there is no flow across the pulmonary vale, and there is streaming of flow into the pulmonary artery as a consequence of retrograde perfusion through the ductus arteriosus
Reference(s):Todros T, Paladini D, Chiappa E, Russo MG, Gaglioti P, Pacileo G, Cau MA, Martinelli P. Pulmonary stenosis and atresia with intact ventricular septum during prenatal life. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 2003;21(3):228–33. PubMed PMID: 12666215.
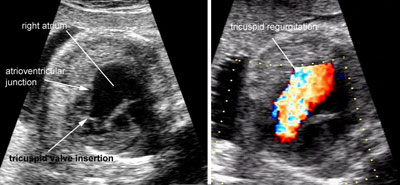
Ebstein malformation of the tricuspid valve
Legend:Ebstein malformation of the tricuspid valve: the leaflets of the tricuspid valve are displaced apically compared to the atrioventricular junction and there is massive tricuspid regurgitation
Tricuspid dysplasia
Legend:Cardiomegaly, enlargement of the right side of the heart and right atrium in particular, massive regurgitation across a normally inserted tricuspid valve
Tetralogy of Fallot
Legend:Tetralogy of Fallot: a large aorta overrides the ventricular septum, the pulmonary artery patent but significantly reduced in size and the right outflow tract is restricted
Reference(s):Paladini D, Rustico M, Todros T, Palmieri S, Gaglioti P, Benettoni A, Russo MG, Chiappa E, D'Ottavio G. Conotruncal anomalies in prenatal life. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 1996;8(4):241–6. PubMed PMID: 8916376. Yoo SJ, Lee YH, Kim ES, Ryu HM, Kim MY, Yang JH, Chun YK, Hong SR. Tetralogy of Fallot in the fetus: findings at targeted sonography. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 1999;14(1):29–37. PubMed PMID: 10461335.
Complete transposition of great arteries
Legend:Complete transposition of great arteries: two great vessels arise in parallel fashion from the base of the heart without crossing; the posterior vessel connected to the left ventricle bifurcates and can therefore be positively identified as the pulmonary artery; the anterior vessel arising from the right ventricle has a long upward course and is the aortic arch
Reference(s):Paladini D, Rustico M, Todros T, Palmieri S, Gaglioti P, Benettoni A, Russo MG, Chiappa E, D'Ottavio G. Conotruncal anomalies in prenatal life. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 1996;8(4):241–6. PubMed PMID: 8916376. Paladini D, Volpe P, Sglavo G, Vassallo M, De Robertis V, Marasini M, Russo MG. Transposition of the great arteries in the fetus: assessment of the spatial relationships of the arterial trunks by four-dimensional echocardiography. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 2008;31(3):271–6. PubMed PMID: 18307212.
Double outlet right ventricle
Legend:Double outlet right ventricle: there is large outlet septal defect and the two great arteries arise side by side predominantly from the right ventricle
Reference(s):Paladini D, Rustico M, Todros T, Palmieri S, Gaglioti P, Benettoni A, Russo MG, Chiappa E, D'Ottavio G. Conotruncal anomalies in prenatal life. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 1996;8(4):241–6. PubMed PMID: 8916376.
Truncus arteriosus communis
Legend:Truncus arteriosus communis: a single large vessel with a thickened valve arises from the base the heart and give rise to the aortic arch and main pulmonary artery
Reference(s):Paladini D, Rustico M, Todros T, Palmieri S, Gaglioti P, Benettoni A, Russo MG, Chiappa E, D'Ottavio G. Conotruncal anomalies in prenatal life. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 1996;8(4):241–6. PubMed PMID: 8916376.
Interrupted aortic arch
Legend:Interrupted aortic arch: there is ventricular disproportion and the ascending aorta is not connected to the descending portion
Reference(s):Volpe P, Tuo G, De Robertis V, Campobasso G, Marasini M, Tempesta A, Gentile M, Rembouskos G. Fetal interrupted aortic arch: 2D-4D echocardiographic assessment, associations and outcome. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 2010 [Epub ahead of print]. PubMed PMID: 20069674. Volpe P, Marasini M, Caruso G, Gentile M. Prenatal diagnosis of interruption of the aortic arch and its association with deletion of chromosome 22q11. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 2002;20(4):327–31. PubMed PMID: 12383312.
Coarctation/tubular hypoplasia of aortic arch
Legend:Coarctation/tubular hypoplasia of aortic arch: ventricular disproportion with dominance of the right cavities, small aortic arch compared to the ductal arch in the transverse view, small and tortuous aortic with the impression of a shelf in the longitudinal views
Aortic stenosis
Legend:Aortic stenosis: hypertrophic left ventricle, thickened aortic valve, slightly enlarged aortic root with high velocity turbulent flow and mitral regurgitation
Reference(s):Paladini D, Russo MG, Vassallo M, Tartaglione A, Pacileo G, Martinelli P, Calabrò R. Ultrasound evaluation of aortic valve anatomy in the fetus. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 2002;20(1):30–4. PubMed PMID: 12100414. Axt-Fliedner R, Kreiselmaier P, Schwarze A, Krapp M, Gembruch U. Development of hypoplastic left heart syndrome after diagnosis of aortic stenosis in the first trimester by early echocardiography. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 2006;28(1):106–9. PubMed PMID: 16795135. Selamet Tierney ES, Wald RM, McElhinney DB, Marshall AC, Benson CB, Colan SD, Marcus EN, Marx GR, Levine JC, Wilkins-Haug L, Lock JE, Tworetzky W. Changes in left heart hemodynamics after technically successful in-utero aortic valvuloplasty. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 2007;30(5):715–20. PubMed PMID: 17764106.
Pulmonic stenosis
Legend:Pulmonic stenosis: severe hypertrophy of right ventricle with little anterograde flow and regurgitation across the tricuspid valve; thickened and poorly opening pulmonary valve; streaming of flow into the pulmonary artery due to the combination of anterograde high velocity flow across the stenotic pulmonic valve and retrograde flow from the ductus venosus
Reference(s):Todros T, Paladini D, Chiappa E, Russo MG, Gaglioti P, Pacileo G, Cau MA, Martinelli P. Pulmonary stenosis and atresia with intact ventricular septum during prenatal life. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 2003;21(3):228–33. PubMed PMID: 12666215.
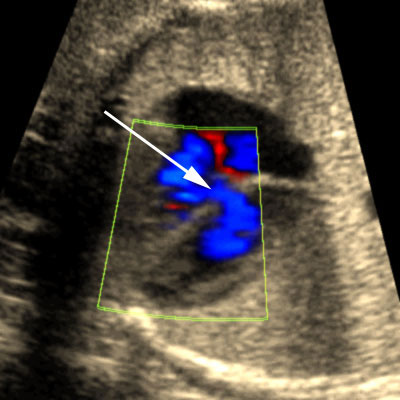
Cardiac anomalies associated with isomerism
Legend:Cardiac anomalies associated with isomerism: common atrium (CA), atrioventricular canal (AV canal) with abnormal connections of the pulmonary veins, parallel great vessels
Reference(s):Berg C, Geipel A, Smrcek J, Krapp M, Germer U, Kohl T, Gembruch U, Baschat AA. Prenatal diagnosis of cardiosplenic syndromes: a 10-year experience. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 2003;22(5):451–9. PubMed PMID: 14618656. Berg C, Geipel A, Kohl T, Smrcek J, Germer U, Baschat AA, Hansmann M, Gembruch U. Fetal echocardiographic evaluation of atrial morphology and the prediction of laterality in cases of heterotaxy syndromes. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 2005;26(5):538–45. PubMed PMID: 16184509. Carvalho JS, Ho SY, Shinebourne EA. Sequential segmental analysis in complex fetal cardiac abnormalities: a logical approach to diagnosis. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 2005;26(2):105–11. Review. PubMed PMID: 16041685.
Left isomerism
Legend:Left isomerism: interruption of the inferior vena cava with azygos continuation
Reference(s):Berg C, Geipel A, Smrcek J, Krapp M, Germer U, Kohl T, Gembruch U, Baschat AA. Prenatal diagnosis of cardiosplenic syndromes: a 10-year experience. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 2003;22(5):451–9. PubMed PMID: 14618656. Berg C, Geipel A, Kohl T, Smrcek J, Germer U, Baschat AA, Hansmann M, Gembruch U. Fetal echocardiographic evaluation of atrial morphology and the prediction of laterality in cases of heterotaxy syndromes. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 2005;26(5):538–45. PubMed PMID: 16184509. Carvalho JS, Ho SY, Shinebourne EA. Sequential segmental analysis in complex fetal cardiac abnormalities: a logical approach to diagnosis. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 2005;26(2):105–11. Review. PubMed PMID: 16041685.
Right isomerism
Legend:Right isomerism: abnormal disposition of abdominal organs; the inferior vena cava is present
Reference(s):Berg C, Geipel A, Smrcek J, Krapp M, Germer U, Kohl T, Gembruch U, Baschat AA. Prenatal diagnosis of cardiosplenic syndromes: a 10-year experience. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 2003;22(5):451–9. PubMed PMID: 14618656. Berg C, Geipel A, Kohl T, Smrcek J, Germer U, Baschat AA, Hansmann M, Gembruch U. Fetal echocardiographic evaluation of atrial morphology and the prediction of laterality in cases of heterotaxy syndromes. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 2005;26(5):538–45. PubMed PMID: 16184509. Carvalho JS, Ho SY, Shinebourne EA. Sequential segmental analysis in complex fetal cardiac abnormalities: a logical approach to diagnosis. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 2005;26(2):105–11. Review. PubMed PMID: 16041685.
Liver in isomerism
Legend:Liver in isomerism
Reference(s):Berg C, Geipel A, Smrcek J, Krapp M, Germer U, Kohl T, Gembruch U, Baschat AA. Prenatal diagnosis of cardiosplenic syndromes: a 10-year experience. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 2003;22(5):451–9. PubMed PMID: 14618656. Berg C, Geipel A, Kohl T, Smrcek J, Germer U, Baschat AA, Hansmann M, Gembruch U. Fetal echocardiographic evaluation of atrial morphology and the prediction of laterality in cases of heterotaxy syndromes. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 2005;26(5):538–45. PubMed PMID: 16184509. Carvalho JS, Ho SY, Shinebourne EA. Sequential segmental analysis in complex fetal cardiac abnormalities: a logical approach to diagnosis. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 2005;26(2):105–11. Review. PubMed PMID: 16041685.